Supply User Manual ENG->Supply Configurations->2.1 LU-SU1101: Instance set-up->A. LU-SU1101: What is an instance ?
A. LU-SU1101: What is an instance ?
When an MSF office (coordination or project) starts using UniField, an instance is prepared for this office by the HQ OC team in collaboration with the UniField core team. An instance is a server (but it can also be called database) which is usually installed on a computer (a laptop) dedicated to UniField. This computer is physically present in the coordination/project office and is maintained by the local IT staff. No user should work on this computer, but it should be accessible through LAN (and sometimes via other means, e.g. Access to an instance can also be granted via other means than LAN, using internet connection, wimax, nano stations team viewer, if a user is not working from the office but needs access to an instance ) in order to allow users from the office to access (and work on) the database from their own work station. A web browser (Mozilla Firefox) is used to access the database thanks to an IP, a user and a password.
If UniField is deployed on an entire mission (migration from previous systems or mission newly opened), several instances are prepared for the mission: 1 for the coordination and n for the n projects of the mission (if it is decided to use UniField on all projects).
If a new project opens-up on an existing mission already using UniField and if the decision is taken to use UniField on this project, 1 instance is created for this project and added to the existing UniField landscape of the mission.
Note that a mission or a project can be opened and UniField installed later on.
When a project or a whole mission using UniField is closing, several operations must be done on the instance(s) before their inactivation.
Different types of instances exist.
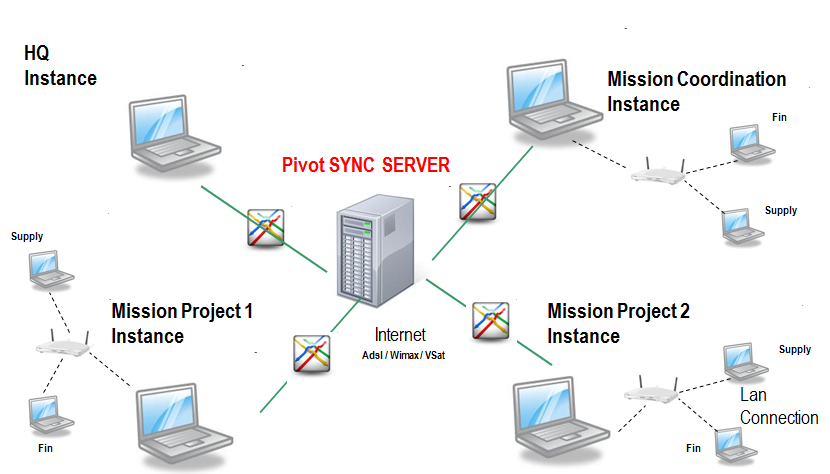
- Coordination and project instances are the ones which are accessed by mission users (supply and finance) to perform their daily tasks. Coordination instances are used in capital while project instances are used at project level. Per mission, you find 1 coordination instance and n project instances.
- Each OC has 1 HQ instance which is usually installed and maintained in the HQ of the OC. The HQ instance is accessed by HQ users.
- Finally, the synchronization instance (also called synchronization server, which can be seen has a pivot) is used to allow exchange of data between instances. The synchronization server is not used to record functional data but only to allow exchange of data between the other instances. There is only 1 synchronization server for the whole MSF movement. Note that project, coordination and HQ instances can be synchronized while the synchronization instance cannot be synchronized.
An order addressed to coordination by a project is pushed to the synchronization server when the project instance is synchronized. It is then pulled from the synchronization server to the coordination instance when the coordination instance is synchronized.
An international product created on a HQ instance is pushed to the synchronization server when this HQ instance is synchronized. It is then pulled to the related coordination/project instances when these related instances are synchronized.
In a supply language, you may say that data exchanged from one instance to another transit through the synchronization server.
The picture below represents the UniField landscape of an OC which would only have 1 mission (with 1 coordination and 2 projects).
 |
| Instances landscape of an OC |
In order for a coordination or project instance to reflect the working environment of the office which it represents, certain parameters need to be configured and some master data (such as the locations or the partners) need to be created before users connect to the database.
