Supply User Manual ENG -> 5. Warehouse -> 5.3 LU-SU4102: Picking -> A. LU INTRODUCTION (LU-SU4102)
A. LU INTRODUCTION (LU-SU4102)
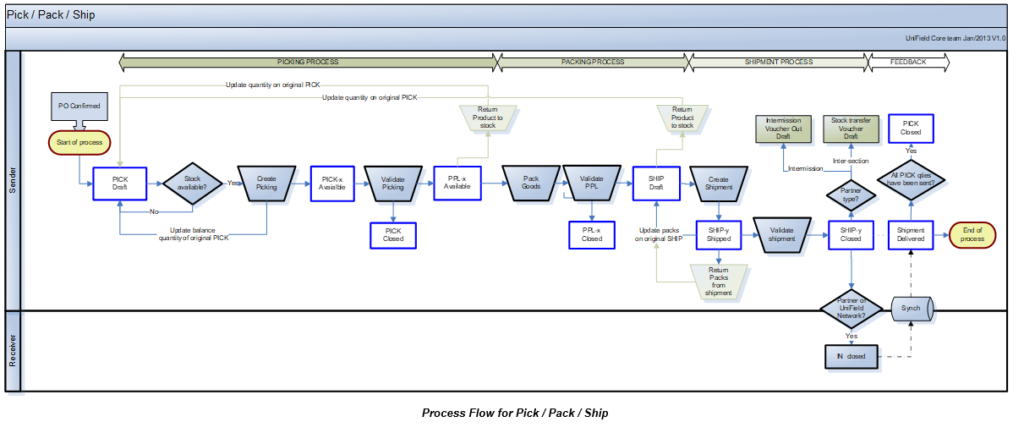
The outgoing delivery is the final step of the process for delivering Field Orders to customers. UniField offers two main options to send goods to customers:
- Simple out, also known as Delivery Order or OUT enables simple and rapid shipments (it takes the goods from stock and ships them directly to customers in a one-step transaction) with very basic documentation.
- Full shipment process offers 2 options:
- “Full flow” progresses through Picking, Packing and Shipment (three-steps transaction) – more common
- “Quick flow” progresses through Picking and Shipment (2-steps) – less common
Both these flows enable to reverse the flow at any stage (returns) and allows the generation of all necessary documentation.
However, this can be changed at any time as Delivery Order can be converted into Picking Tickets and Picking Tickets can be converted into Delivery Orders.
Note that the configuration of an instance can be changed so that the full shipment process is not used. In this case, all deliveries will be done with the simple out process.
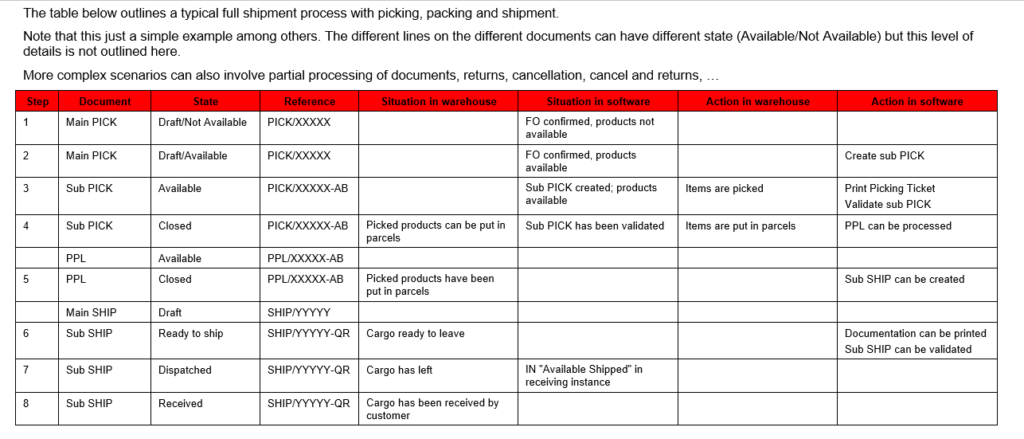
Picking is the process of taking products off the shelves of the warehouse and preparing to pack them. Picking Tickets are created in “Draft” when Field Orders (or Field Order lines) are confirmed. Then they need to be processed manually. In UniField a Picking Ticket cannot be created from scratch, but is created by the system as it is always directly linked to a specific FO.
- If an FO (or FO-line) is sourced from stock, a Picking Ticket is created in the state “Draft” and is “Available“ (provided that the products are indeed available in stock).
- If an FO (or FO-line) is sourced on order and to a PO, a Picking Ticket is created in the state “Draft” and is “Not Available” (but only when the related PO (or PO-line) is confirmed as it will also confirm the corresponding FO (or FO-line)).
In both cases, the Picking Ticket created is named main PICK or parent PICK and will have a reference which looks like PICK/000XY. When this main/parent Picking Ticket will be processed, sub PICKs will be created with a reference which looks like PICK/000XY-AB.
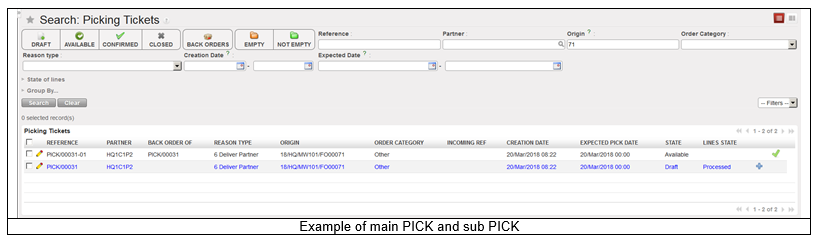
The main/parent PICK will always remain open in “Draft” state (until final shipment is done). It will be used to create additional sub PICKs in case of partial pickings, or to manage the return of the products back to stock, in case of an unpacking process.
The picking process is done in several steps:
- A main Picking Ticket is created (or updated) by the confirmation of the FO (or FO lines). This allows the warehouse team to see in the system which products/quantities/batches will have to be picked in the coming days or weeks. Virtual stock levels are updated.
- A sub Picking Ticket is created from this main Picking Ticket in order to instruct the storekeeper to actually pick products/quantities/batches.
- Once the actual picking has been done in the warehouse, the sub Picking Ticket is validated (and possibly updated) with the actual quantities and batches which have been picked. Picked products/quantities/batches are transferred on a Pre-Packing List. Real stock levels are updated accordingly.
The creation of the main PICK updates the virtual stock levels, decreasing the virtual stock level of the source location (from where the goods will be picked) and increasing the virtual stock level of the “Packing” location. The validation of the sub PICK updates the real stock levels of both locations.
Main PICKs are actually never validated. They are just used to initiate the picking process, allow partial picking on main PICKs, allow partial validation on sub PICKs and allow returns from Pre-Packing Lists.