Supply User Manual ENG -> Products -> 3.1 Products in UniField -> B. Product Record tabs, sections and fields
B. Product Record tabs, sections and fields
In the following section, the Learning Unit will detail each of the tabs, sections and fields included in the Product record as well as describing any relevant conceptual background.
- Information tab
Go to: Products / Products
- Open a Product record by clicking on the line or on the pencil icon
 (to open it in edit mode) or click on “New” to view these fields in an empty product record
(to open it in edit mode) or click on “New” to view these fields in an empty product record - In the header of the Product record, there are fields for the product’s Code and Description
- Code refers to the UniField product code – Please refer to the MSF Logistic Catalogue/UniData Guidelines for more details of code composition. The composition of the code is not enforced by the system, but a string of recognised characters can be added freely, so users should ensure this is correct before the code is created.
The only added constraint is that UF requires that the locally created product contain a “Z” in their naming.
- Description, refers to the UniField description – Please refer to the MSF Logistic Catalogue / UniData Guidelines for more details of description composition
- Old Code, refers to previous code (depending on codification and system) this code will have be replaced by the current one.
- New Code, refers to the new code (e.g. if current code is now obsolete and there is a new code/product which should be used/ordered in its place)
3. Under the Code and Description fields, there is a set of tabs; Information, Nomenclature, Dates, Specific info, Miscellaneous, Suppliers, Descriptions, Procurement & Locations and Accounting.
In each tab, there are different sections. In the information tab there are sections on Procurement, Prices, Dates, and in each of these contains one or more fields.
The system will trigger different alerts, processes and tools according to the type of product and attributes entered in these fields.
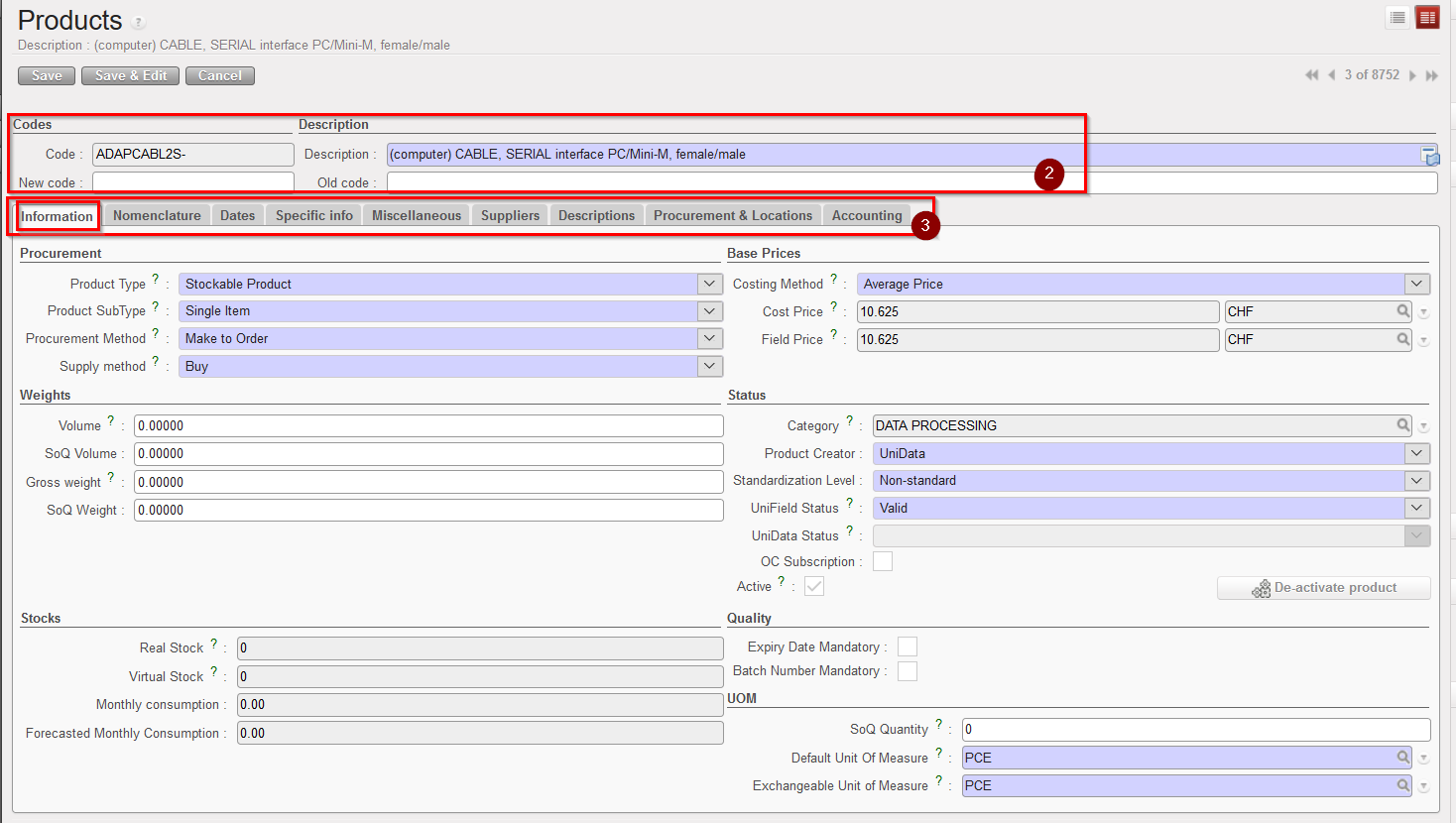
Information tab
4. Procurement section
This section covers the different elements which the system needs to know in order for a product to be purchased, as different products will trigger different procurement processes within the system. A product could be stocked in large quantities or not be stocked because the requester may not need the product, but has simply ordered it for another project, or because the product was only needed once and no regular consumption is foreseen.
The information needed in order to procure the product is as follows:
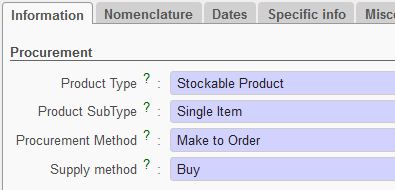
Product procurement types
- Product Type:
- Stockable product, for products which are usually in stock and can be stocked
- Non-stockable, for products that we will not be managed in the storage and dispatch stages of the system (e.g. stationery, expat food etc). Non-stockable products should be received in the “Cross docking” location if they have been requested by another project as explained above. Otherwise, they will be received by default, directly in the virtual location “non stockable”. They will remain in the temporary locations and be transferred from there to the requester (no Internal Moves or movements to another location within the same instance).
- Service with reception, for products which are services, such as construction, transport and electricity services, etc. This option is explained in more detail later in this chapter. We need to receive a product as a service for the system to generate a reception document which finance department need to verify before clearing and paying any invoice.
If this Product type (Service with reception) has been selected, a checkbox called “Transport product” will appear. This should be ticked if the service is a form of transport – e.g. freight, as this will allow the user to generate reports on transport costs. Services with reception will by default be received into the virtual location “Service”. These products should never be received into a Cross-Docking location, as they should be ordered on a Direct Purchase Order if ordered for another instance.
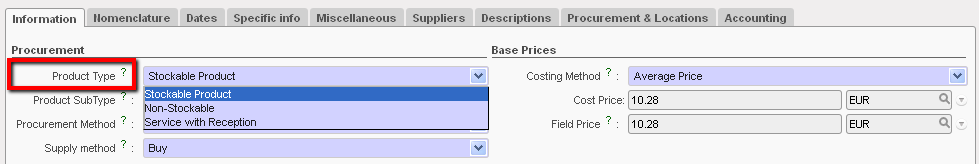
Product Type
- Product Sub Type (will appear if Product type has been selected as stockable)
- Single item, this is used for almost all the products which can be measured as a countable unit (e.g. a blanket, oral drugs etc).
- Kit/Module, this option is used for kits (containing more than one product and/or module in the package or box).
- Asset Should be selected when the product is an asset. This will trigger other fields/processes to become mandatory in the system in order to facilitate sufficient tracking of assets. If a product is an asset, it must be recorded in the system as such, as assets require special attention. Assets need to be identified, tracked, repaired and disposed of with a greater level of detail than other products. Please refer to your OC procedures to understand which products should be classified as assets. If the asset checkbox is ticked in the product record, the system will require further information relevant to the asset (e.g. brand, model etc) to be entered into the system at certain points (e.g. at point of reception).
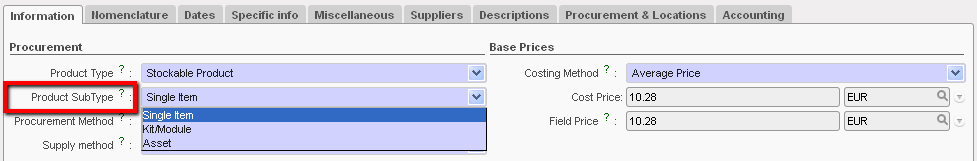
Product Sub-Type
Asset Type
It is mandatory to select the asset type if Product Subtype is an “Asset”. The options are:
- IT
- Transport
- Medical
- Telecommunication
- General
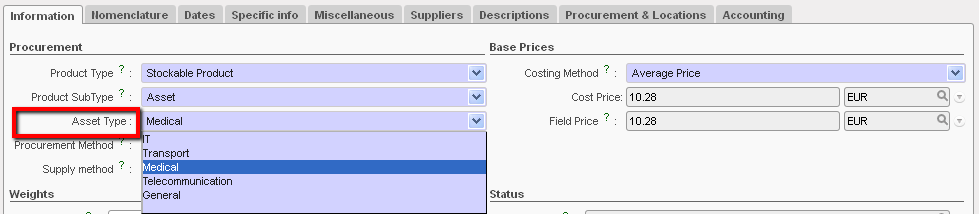
Asset type
- Procurement Method
- Make to order, is the option for products which are not consumed on a regular basis, so no replenishment rules are applicable and any request for these products would be raised manually according to a specific need. Therefore, a request for one these products would be made via an Internal Request (if it can be sourced within the same instance) or via a Field Order (if ordered to a parent instance).
- Make to stock, is the option for products which are regularly used, so generally this should be selected where the replenishment rules have been set (see Chapters on Inventory Management and Configuration) which will lead to the system automatically creating draft
POs for these products.
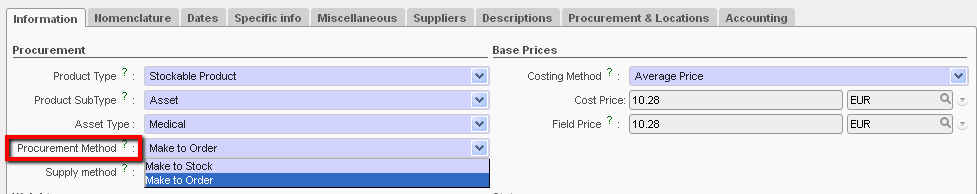
Product Procurement Method
- Supply Method
- Buy: most products in MSF will be bought so we will often use “Buy”. All services will have “Buy” as the Supply Method.
- Produce: this option should be used when MSF needs to create a product (most likely to produce a kit)
- Base Price Section
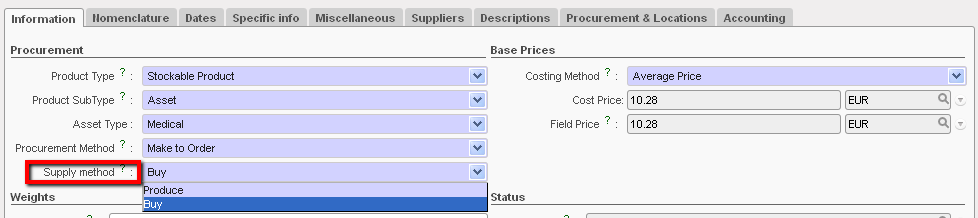
Product Supply Method
5. Rubrique « Prix de base »
Product Base Price
- Costing Method
- Average Price: this option should always be chosen. It is calculated according the Moving Average Cost (MAC) principal and uses the average value of the product in stock and takes account of all recent prices paid for this product within the instance. When an Internal Request is created for a product, the system will automatically pull this price for the product, although this default price can of course be edited/changed. The same is true for a Purchase Order where there is no active Catalogue for the Supplier.
- Standard Price: this option indicates that the price of the product is fixed and doesn’t change (some products procured from ESCs). However, this option should NOT be used.
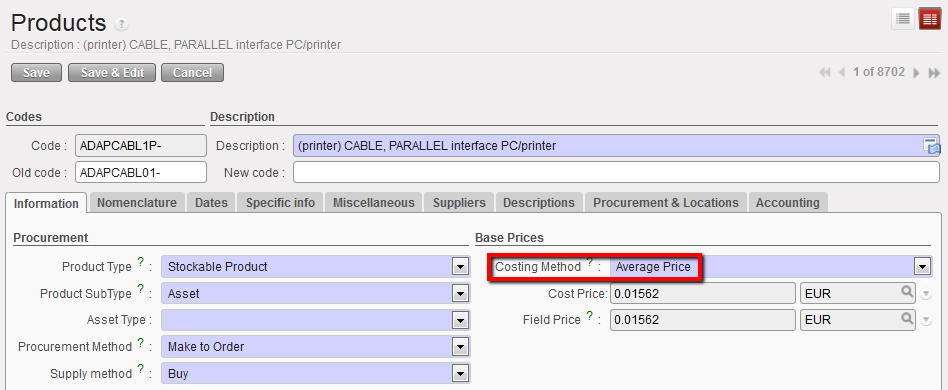
Costing Method
- Cost Price
This is the price of the product based on the costing method selected above (i.e. Average price).
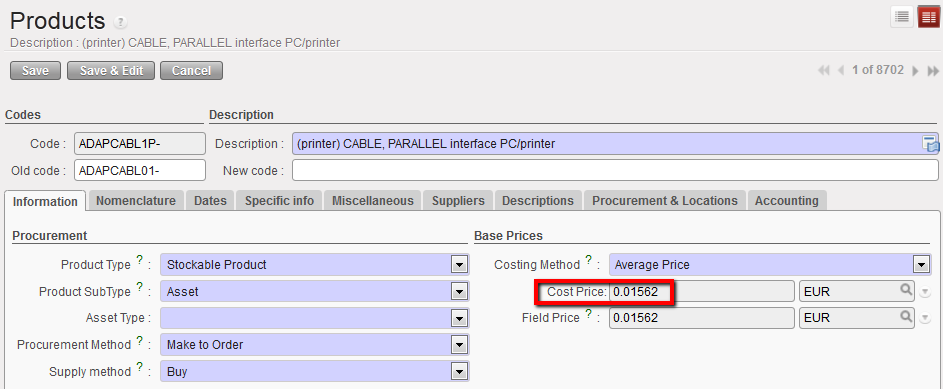
Cost Price of a Product based on the Costing Method chosen
- Field Price
In the situation where a product is sourced from an RSC (Regional Supply Centre), the field price will equal the cost price plus a percentage (e.g. +2%) to cover the service that RSC provide in sourcing the product.
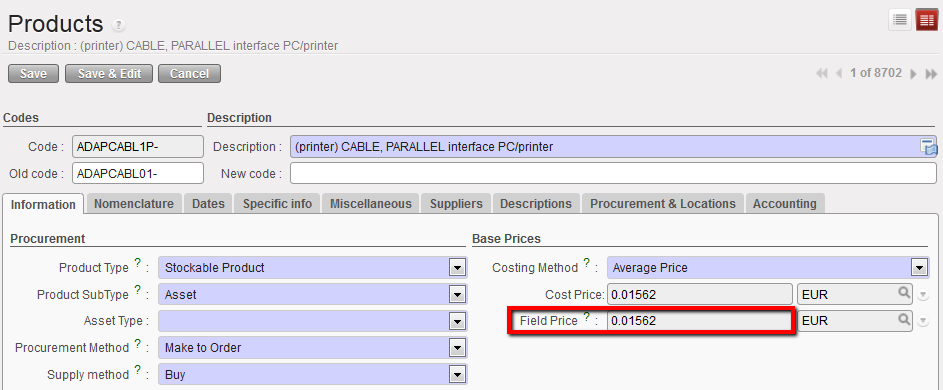
Field Price
6. Weights Section
It is useful to fill in as much of this information about the product (Volume, SoQ Volume, Gross Weight, SoQWeight) as possible in order to help the system calculate cargo volume, which will have an impact on transport, storage and therefore on the cost. The SoQ Volume and Weight figures should be based on the quantity as designated in the UoM section “SoQ Quantity” if one exists. See below for further explanation of this.
7. Status Section
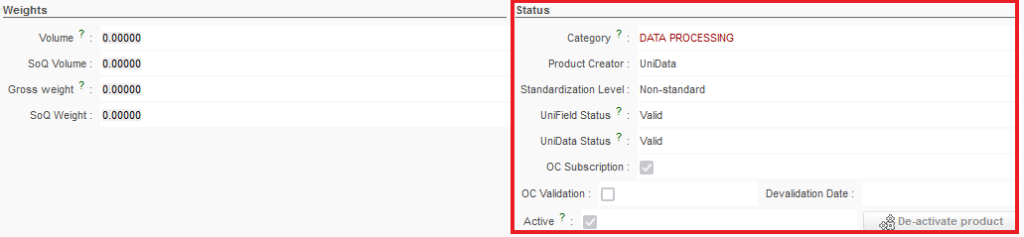
Product Status section
- Category
This is an important field and it relates to the Product family. The option displayed is selected by default and will impact the Expense and/or Income accounts in Finance. You will not be able to modify the option in this field as it will be generated according to the Family selected (in the Nomenclature tab), but if you need to change the Family of the product then this may change the default Category.
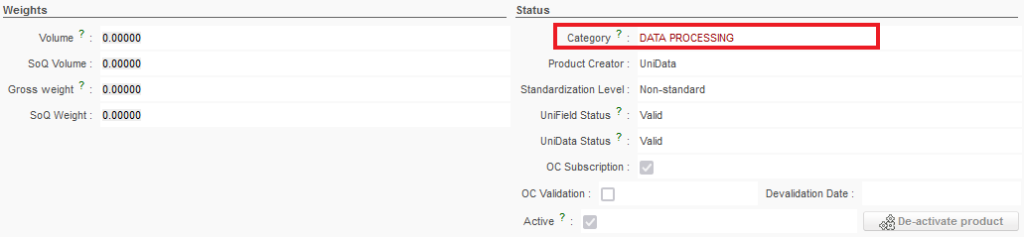
- Product Creator
This indicates who created the product. If it is a standard product (it is recognised by UniData / the MSF Logistics Catalogue) then it will be created by UniData and there will be complete visibility of it across all instances via the synchronisation process.
- UniData – synchronised (if all OCs have subscribed in UniData then it will be common to all HQs & missions). The majority of products in instances are UniData.
- ITC – synchronised (common to all HQs & missions) – these are being cleaned and replaced by UniData codes
- ESC – synchronised (common to all HQs and missions who use the ESC) – these are being cleaned and replaced by UniData codes
- HQ – synchronised across the OC
- Local – Created in coordination instance and will be synchronised within the mission (being cleaned as well and to be replaced by UD products)
- Temporary – to be considered only as a “draft” status for newly created products – not synchronised and should not be added to any orders.
- Standardization Level, this is a specific property linked to the Unidata / Codification document. Please refer to Unidata Documentation for more details.
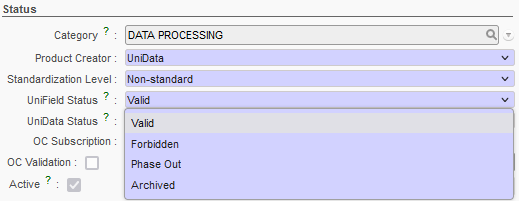
- UniField Status
Linked to the product life cycle and to projects (This is linked to the UD / codification project and should be used only in accordance with agreed procedures). UniField Status updated following synchronisation from HQ which is itself stemming from UD linkage ( following agreed mapping – see internal procedures).
Therefore, “UniField status” is now dependent on “UniData Status” (see next paragraph) however, only “UniField Status” will still have a functional impact in the system.
- Valid – Can be used as a normal product; can be ordered, stocked and consumed (Active)
- Phase Out – Can be stocked and consumed normally, but ordering is limited to only internal partners (i.e: excluding as well ESCs) (Active)
- Archived – cannot be ordered, stocked or consumed (Inactive)
- Forbidden – cannot be ordered, stocked or consumed in the field. To move to quarantine/Destruction (or Internal FO from Stock) (Active)
This value is filled only for UniData products and is added via the linkage from UniData at HQ level which is then synchronized to the fields. It is a read only field, it cannot be changed/updated by UF users or OCs. A mapping document enables to match the UniData Status to the UniField Status. Please refer to UniData guidelines for how this can be used and the impact on the “UniField Status” field (UF UD Product lifecycle mapping).
As a reminder, the “UniData Status” has no direct functional impact on the system but its impact on the “UniField Status” will functionally impact the system.
NB: UniField is responsible to cross-check and follow the mapping according to the received “UniData Status” and “OC Subscription” and then to update the “UniField Status” and “Active” checkbox fields where relevant (see below points “Active” and “OC Subscription”)
As soon as a product on a UF HQ instance has its field “OC Subscription” unticked or “UniData Status” = “Archived”, a UF mechanism will aim to deactivate it and may update the UniField Status. If the product has stock or pipe or is in a Product list, the product is kept active and its UniField Status is set to “Phase Out”( temporary status). If the product is not in pipe nor in stock nor in a product list, an automatic batch will inactivate the product and set its “UniField Status” to “Archived”.
- OC Subscription (checkbox)
This information is read only as well and linked only to UniData products. It will indicate whether the product has been subscribed by the OC in the UniData interface ( see your OC UniData guidelines for more details).
To note that Unsubscribed UD product should be updated in UF either as Inactive- Archived (if no more product in the instance) or Active-Phased Out (in case products are still in Stock or Pipeline).
- OC Validation (checkbox)
This information is read only as well and linked only to UniData products. It will indicate whether the item is Validated by the OC (included in the OC’s MML).
- Devalidation Date
If a product is devalidated (removed from the MML), the devalidation date will be shown here.
- Active (checkbox)
This is very important, as it should be ticked for the product to be active (i.e. be recognised and visible) in the system. If this box is not checked, the product cannot be ordered, viewed in stock, dispatched, etc. (this box is automatically checked when a product is created except for UD non standard local product at mission level)
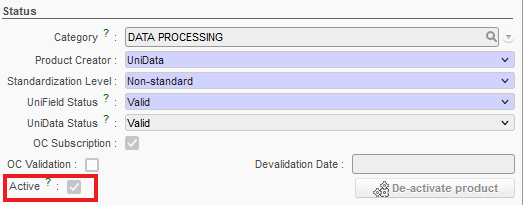
Please note that in the Products Search View the default filter is on Active products.
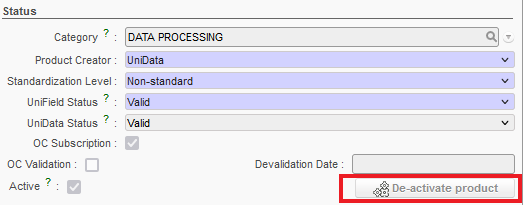
- De-Activate Product
This button allows the product to be de-activated when it is not being used in the system (in an open Supply document) or when it is present as stock in an internal stock location (see later on in this chapter for How to de-activate a product for more details).
8. Stocks section
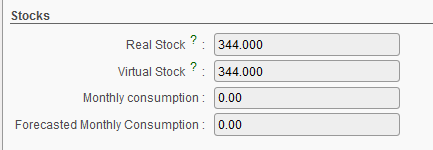
Product stocks section
Stocks will be calculated by the system, the user cannot edit these fields.
- Real Stock: quantity computed in real stock, this includes products in locations: LOG/MED in main stock AND all configured Internal locations (Intermediate stock and Internal consumption units). AND E-Prep internal locations.
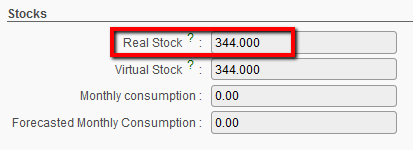 Real Stock
Real Stock
- Virtual Stock: quantity computed in virtual stock (same locations as for Real stock above) i.e. as soon as a product was received in the Input location and before it was assigned to a stock location.
 Virtual Stock
Virtual Stock
- Monthly consumption: view of stock consumed (or which has left the system) for one month during the past 3 months
Monthly Consumption
- Forecasted Monthly Consumption: estimation of the quantity of the product which will be consumed over a month. This information is calculated according to the monthly consumption report and comes from what has been entered (manually) for this report
Forecasted Monthly Consumption
9. Quality section

Quality section : Expiry Date and Batch Number
- Expiry Date Mandatory:
Most medical products will come with a batch number and expiry date. UniField has very good tools to analyze and manage these products. This information must be recorded manually in the system at the time of arrival of the products to ensure full system capability. Many UniData/ITC/ESC/HQ products will have this option enabled. See Unidata / OC guidelines for how this attribute should be managed.
The checkbox “Expiry Date Mandatory” should be ticked for all medical products and perishable products with an expiry date, For UniData products, this attribute will be set according to the OC’s stated preferences (please refer to UniData / OC guidelines).
This checkbox is only editable at HQ (for UniData/ITC/ESC/HQ products) and at Coordination with specific user rights (for Local products).
Whenever this attribute is changed/ updated, information will be synchronised down to children instances and stock/ transaction with this product will be updated (i.e: if ED attribute removed then the existing ED will be deleted; if ED attributes added then new ED will be automatically added “ED = 31/12/2999 and will need to be changed later by the user). Please note that there is a way to update this attribute in mass if necessary (see below).
 Please note: Expiry dates are a very important detail of a product, it’s crucial that this information is accurate.
Please note: Expiry dates are a very important detail of a product, it’s crucial that this information is accurate.
Batch numbers are necessary for some products to indicate production batches, or the manufacturer’s batch reference number. Similarly to expiry dates, it is very important that batch numbers are accurately recorded and that we have good visibility on them. This information must be recorded manually in the system at the time of reception. This number will be used throughout the product life until it has been used / consumed.
The checkbox “Batch Number Mandatory” should be ticked for most medical products as well as many other types of products for which it is useful to differentiate between batches in order for products to be managed efficiently. As with Expiry Dates (see previous description) for UniData products, this attribute will be set according to OCs’ stated preferences.
This checkbox is only editable at HQ (for UniData/ITC/ESC/HQ products) and at Coordination with specific user rights (for Local products).
Whenever this attribute is changed/ updated, information will be synchronised down to children instances and stock/ transaction with this product will be updated (i.e: if BN attribute removed then the existing BN will be deleted; if BN attributes added then new BN will be automatically added “BN = TO-BE-REPLACED” and will need to be changed later by the user). Please note that there is a way to update this attribute in mass if necessary (see below).
10. UoM section
Product UoM section
This is for the Standard Ordered Quantity which represents the quantity in which this product is usually ordered, this could be based on packaging or grouping of the product. When the field is filled with a value, this figure can be used by the system, on command, to round up the quantity in Internal Requests or in POs and FOs (see Procurement Chapter for more information on this)
- Default Unit Of Measure
UniField supports several Units of Measure (UoM). The same product can be expressed in different units of measure. For example, you can buy grain by ton and distribute it by kg. To do this, it is important to ensure that all the units of measure used for a product are in the same UoM category. It is not possible to convert something which has a UoM of Kg into cm as these 2 UoMs belong to different categories. If a product has a UoM which belongs to a weight category, it can only be converted into another weight category UoM. Kg could then be converted into tons or grams for example.
Default UoM

Please note: All units of measure in the same category are convertible from one unit to another
Some examples of Units of Measurement in the system:
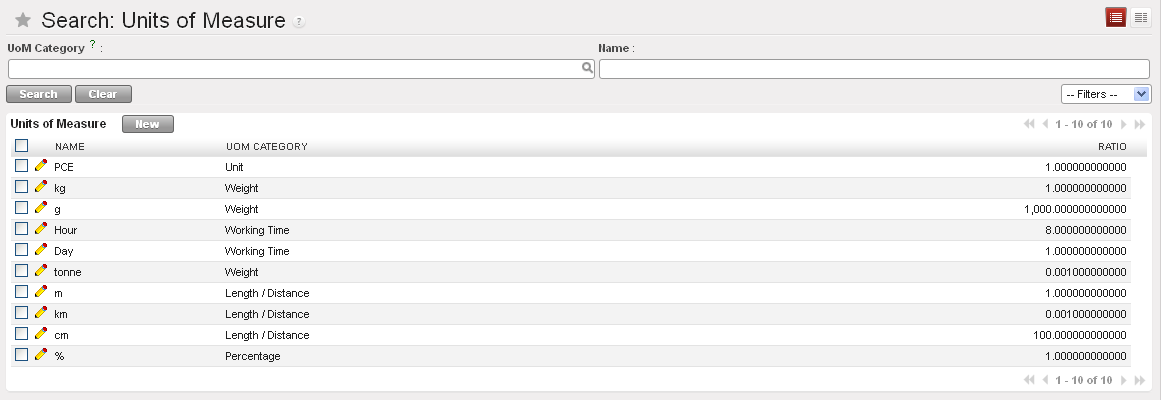
UoM
The table below shows some examples of units of measure and their category. It is possible to convert from one unit of measure to another as long as they are in the same category.
Sample of Units of Measure (UoM)
| UoM | Category | Ratio | UoM Type |
| Kg | Weight | 1 | Reference |
| Gram | Weight | 1000 | Smaller |
| Tonne | Weight | 1000 | Bigger |
| Hour | Working time | 8 | Smaller |
| Day | Working time | 1 | Reference |
| Half-day | Working time | 4 | Smaller |
| Item (PCE) | Unit | 1 | |
| 100 Items | Unit | 0.01 |
Product Units of,Measure
In the table above you can see 1Kg = 1000g = 0.001 Tonnes. A product in the Weight category could be expressed in Kg, Tons or Grams. You cannot express it in hours or pieces.
To define a new unit of measure, go to: Supply Configuration/ Products / Unit of measure /Units of Measure and Select New.
New button to create a UoM
In the definition of a Unit of Measure, there is a “rounding precision factor” which shows how amounts are rounded up or down after the conversion. A value of 1 would be rounded to the level of one unit. 0.01 means the product would be rounded to one hundredth of a unit.
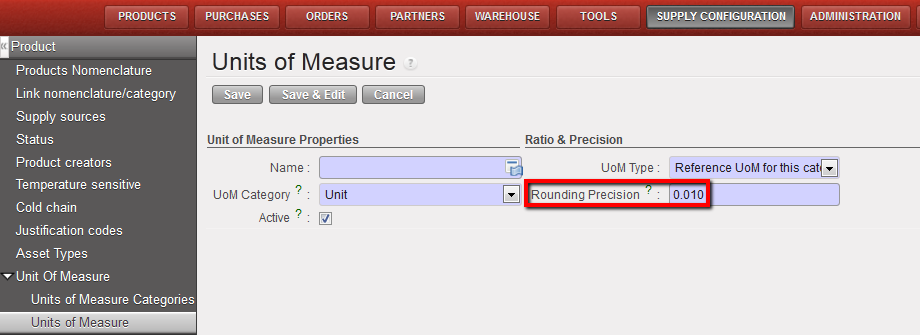
UoM Rouding Precision
- Exchangeable Unit Of Measure
While the “Default Unit of Measure” is mandatory for all products, the “Exchangeable Unit of Measure” is optional, and should be convertible from and to the default unit of measure. This means that if, in most cases you will buy, store and deliver grain in tons, then tons will be your default UoM, and if you need to sometimes deliver the grain in smaller quantities measurable in Kg, then this should be set as the Exchangeable Unit of Measure.
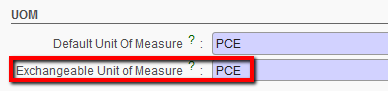
Exchangeable UoM

Please note: For services, the UoM could be set as Working time or Distance or Percentage. At PO creation, when “service” is selected, the “Unit of Measure” may be set to percentage and the unit 100%. This is because it is common to pay for services in quotas, and this way, a percentage of the total can be paid when required.
When deciding on the UoM, it is important to think about the units in which the item would usually be requested (i.e. on the PO/FO), the units in which it will be stored, and the units in which it will be delivered..
Detailed information on ITC product UoM is available in the MSF Logistic Catalogue.
2. Nomenclature tab
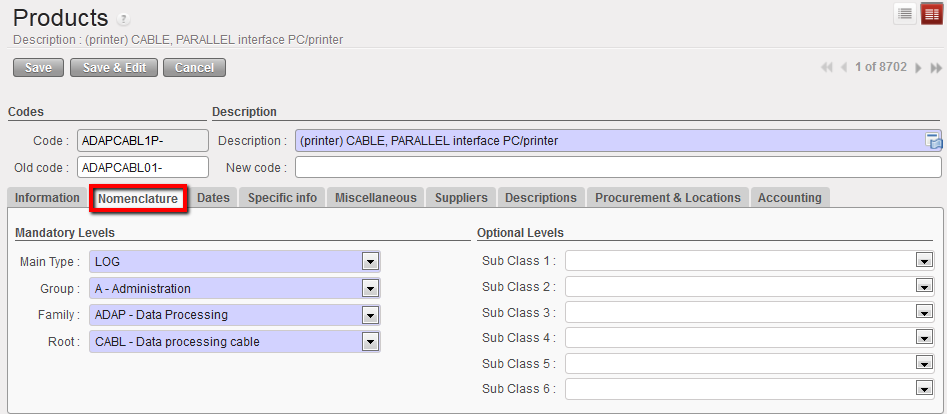
Nomenclature tab of a Product form
Nomenclature is the structure of the name of a product. It is used to classify and describe products per type, group, family and root. These attributes will categorise the product. As you can see in the picture below, the system also provides optional levels as such as sub classes. We recommend entering as much information as possible about the product in order for the system to provide as much accurate information as possible.
a. Mandatory Levels section
The mandatory levels can only be created or edited by the instance owner (coordination or higher); in most cases, users won’t need to make changes to these. Please see the MSF Logistics Catalogue/ UniData guidelines for more details on Main Type, Group, Family and Root.
Please note that the selection of the family value will be visible in the Category field in the Information Tab, and this has an impact on the expense / income accounts in Finance.
b. Optional Levels Section
If additional classification is needed in the future, there are six Sub Classes which can be added (refer to specific OC guidelines for more details).
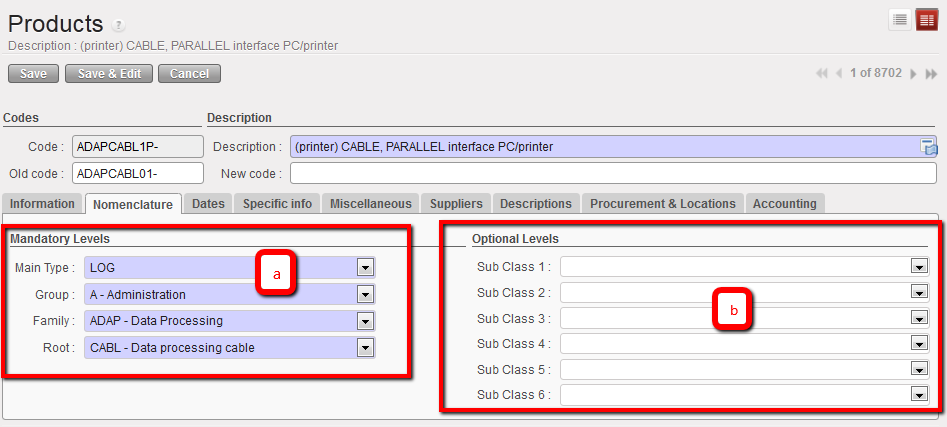
Product Nomenclature tab
Please note: The nomenclature tab can also be used to order a product at field level if the product isn’t listed in the UniField database.
This option is explained in detail in LU-SU3201 PO General, “How to create a Purchase Order by nomenclature (previously known as * product)”

3. UD OC Validation Tab
The information in this tab provides a summary of MML/MSL information linked to this product.
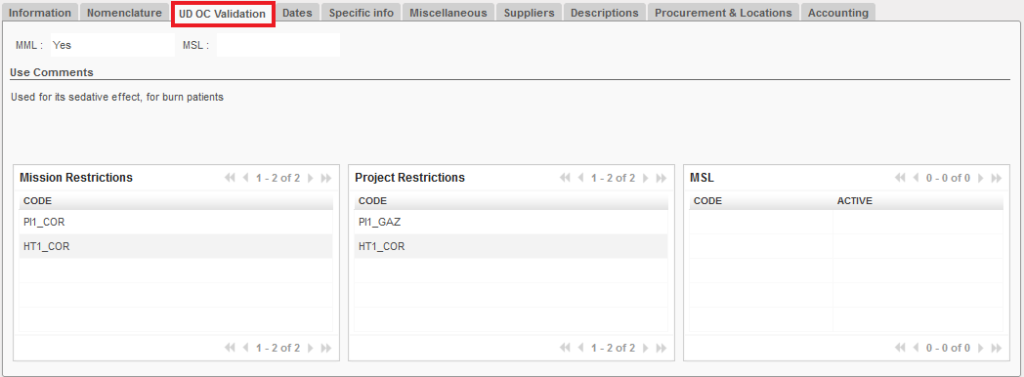
MML & MSL:
The two boxes at the top of this section indicates whether or not an item is included in the Medical Master List (MML) and/or Medical Standard List (MSL).
The MML field will always be filled for medical products. “Yes” will be shown as long as the product is included in the MML, even if it’s restricted to specific projects/countries.
The MSL field will show a value (Yes / No) only if the MSL is activated. If there is no active MSL linked to that instance, the MSL field will be blank (like in the image above).
Use Comments:
Use comments are taken directly from the UniData MSL Tool. This field contains a variety of information, from details about when/how to use of this product to procurement information (for example, if an item is Local Purchase only) to ranking and product alternatives. As this information is pulled directly from an external tool, this information is not translated.
Mission Restrictions:
If a product is limited to a specific mission for an OC, the mission code to which this item is restricted will be listed in this section.
Project Restrictions:
If a product is limited to a specific project, the instance code of the project to which this item is restricted will be listed in this section.
Note: Project restrictions are encoded separately from the MSL, so it is possible for a product to be restricted to a specific project without being in that product’s MSL.
MSL:
This section will list the code of any projects in the same mission that include this product in their MSL. If the MSL is active, there will be a check in the checkbox for that project. If not, the checkbox will be empty.
4. Dates Tab
This information is useful when a product has a finite or recommended limited life, which may be longer than an expiry limit, but can be used for calculations relating to replenishment, storage or even budget preparation.
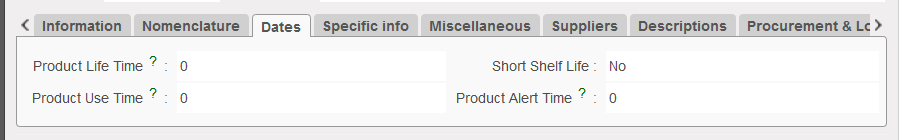
Product Dates tab
All appropriate fields should be completed:
- Product Life Time, this field will be active if the Short Shelf life is set to Yes
- Product Use Time, to indicate the time period within which the product should be used (should be smaller than the Product Life time).
- Short Shelf Life (check box), if this is ticked in a product, when this product is ordered, an alert will warn the user that due to its short self-life, it should be ordered quarterly and to take care with transport mode and lead time.
- Product Alert time, period of time set for product when, if it is in stock, system will alert user about this batch / group of products.
5. Specific Information tab
a. Quality Section
- Temperature Sensitive items
Please refer to UniData Guidelines / MSF Logistics Catalogue for more information on these attributes. The options selected regarding temperature will have an impact on the picking / transport and storage transactions. (e.g. when receiving an incoming shipment of products which have these qualities, the system will display alert that this status should be considered when storing / transporting products).
The following information should be selected if it is relevant to the product. Most of the time, this information can be found in the product documentation. If “Yes” is selected for Temperature Sensitive Item, then the field “Thermosensitivity” becomes visible and active.
- Thermosensitivity: Current values
0208 0208 Cold Chain / Refrigerated 2-8°C 1525 1525 – Controlled Room Temperature 15-25°C CT25 CT25 – Controlled Temperature 2-25°C CT30 CT30 – Controlled Temperature 2-30°C F-20 F-20 – Frozen <-20°C FSRT FSRT – Frozen for Storage, Refrigerated for Transport Below: Old Thermosensitivity values which are still present in UniField (most products have had old values migrated to the values above):
- * – Keep Cool: used for a kit or article containing cold chain module or item(s)
- *0 – Problem if any window blue
- *0F – Problem if any window blue or Freeze-tag = ALARM
- *25 – Must be kept below 25°C (but not necessarily in cold chain)
- *25F – Must be kept below 25°C and cannot be frozen: check FreezeWatch
- *A – Problem if A, B, C and/or D blue = ALARM
- *AF – Problem if A, B, C and/or D blue or Freeze-tag = ALARM
- *B – Problem if B, C and/or D blue = ALARM
- *BF – Problem if B, C and/or D blue or Freeze-tag = ALARM
- *C – Problem if C and D blue
- *CF – Problem if C and/or D blue or Freeze-tag = ALARM
- *D – Store and transport at -25°C (store in deepfreezer, transport with dry-ice)
- *F – Cannot be frozen: check FreezeWatch.
Products with Thermosensitivity value 0208 * are tagged as “Cold Chain” and when they are received (via an Incoming Shipment) there will be a warning message on screen that user is receiving a heat sensitive product and should refer to the appropriate procedure. Additionally on all stock moves, any product with this Cold Chain attribute will have the checkbox “CC” ticked.
*There may be some products not yet migrated to the new Thermosensitivity values, but if they have the equivalent old value of 0208 they will also be flagged as Cold Chain with warning on IN and CC checkbox ticked.
- Sterile, as per details of products
- Single Use as per details of products
- Controlled Substance as per details of products. Box needs to be checked for products of this category since it will have an impact on customs and documents to be produced.
One of the following attributes should be selected according to the product:
- ! – Requires national export license
- DP – Drug precursor
- N1 – Narcotic 1
- N2 – Narcotic 2
- P1 – Psychotrop 1
- P2 – Psychotrop 2
- P3 -Psychotrop 3
- P4 -Psychotrop 4
- Y – Kit or module with controlled substance
- CS / NP – Controlled Substance / Narcotic/Psychotropic
- Blank
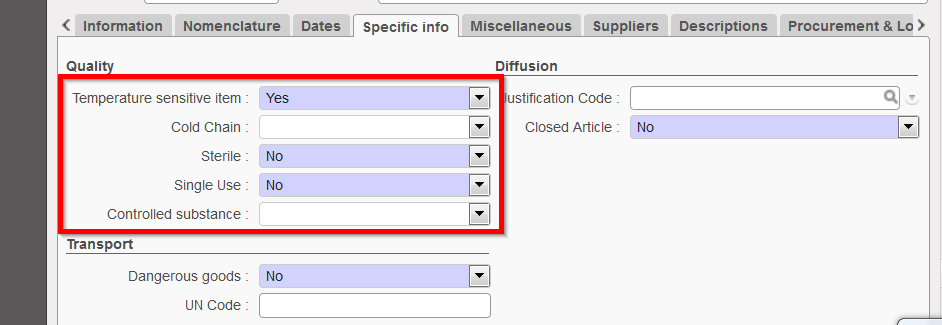
Quality section
- Diffusion section
The following fields are to be entered according to the product procedures (refer to OC for more guidance).
- Justification Code, as used as in previous system in place. This is used in case a product has to be justified. It displays justification codes A, E, F, M. These codes give the reason why the order has to be justified.
- Closed Article, Yes/No. If yes, it indicates that there is a mandatory manufacturer. This will be implemented with the new ITC database.
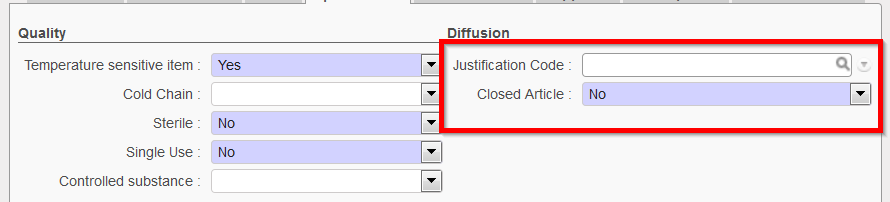
Diffusion section
b. Transport section
- Dangerous Goods (Checkbox), as with the temperature status, the activation of this checkbox will lead to an alert being displayed on all picking / transport & storage transactions.
- UN Code, can be added if known.
- HS Code, this harmonized system code will be pulled from UniData and synced down to all instances below.
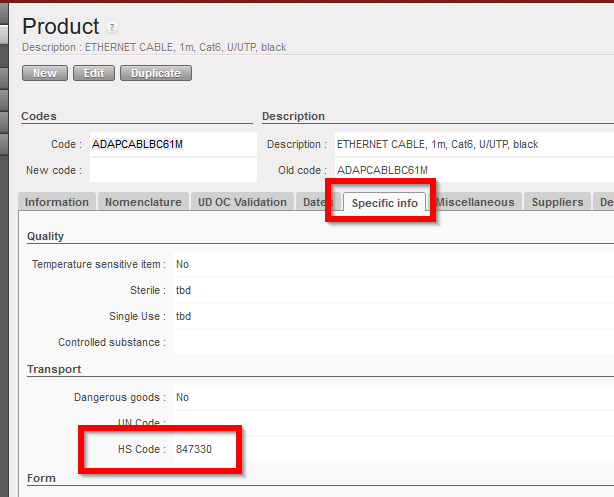
Transport section
- Import Restrictions section
The check box Restricted in the Country and the field County Restriction can be activated if the instance has been configured with one or more restrictions (See Configuration Chapter for more details). Once this has been configured, it will be possible to activate and select the restrictions relevant to the Product.
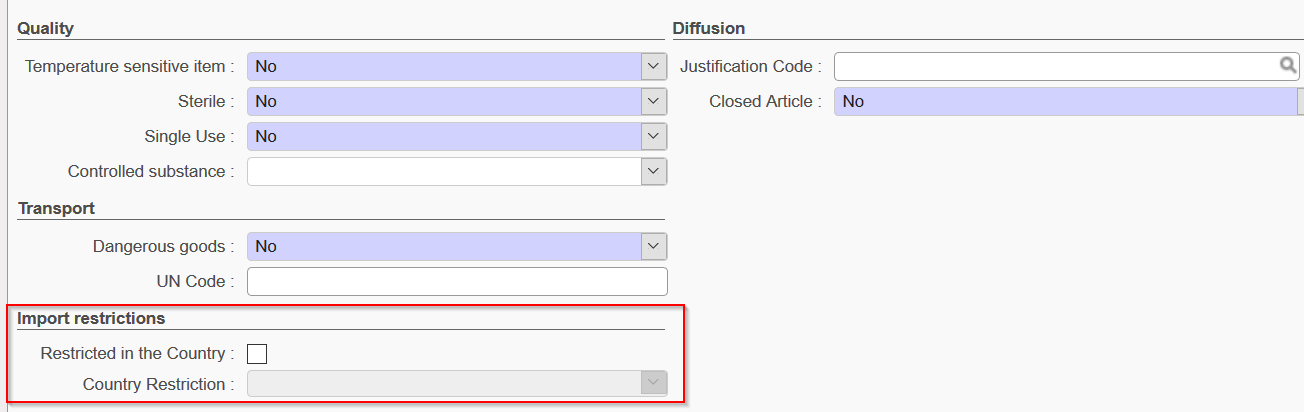
Import restrictions sectio
Form, Fit & Function section
These fields are product properties related to the Unidata /Codification project. Please see Unidata documentation for further details. The original value will be synched with the product as will any update made to these fields.
Form, Fit & Function fields
- Miscellaneous tab
- Information section
- Criticality, as per guidelines this gives the level of attention required to manage (supply) a product. (1 Exceptional, 5 Common etc)
- ABC Class, as per standard item classification
3. Lists/Sublists section
This field will indicate all lists and sublists where the product appears
4. Code remarks section
- Supply source , the system will display three types of sources:
- International
- Local
- Non local
6. Miscellaneous / Associated Products Section
This should list any products which are associated with the main product, e.g. products part of a same kit composition list, etc.
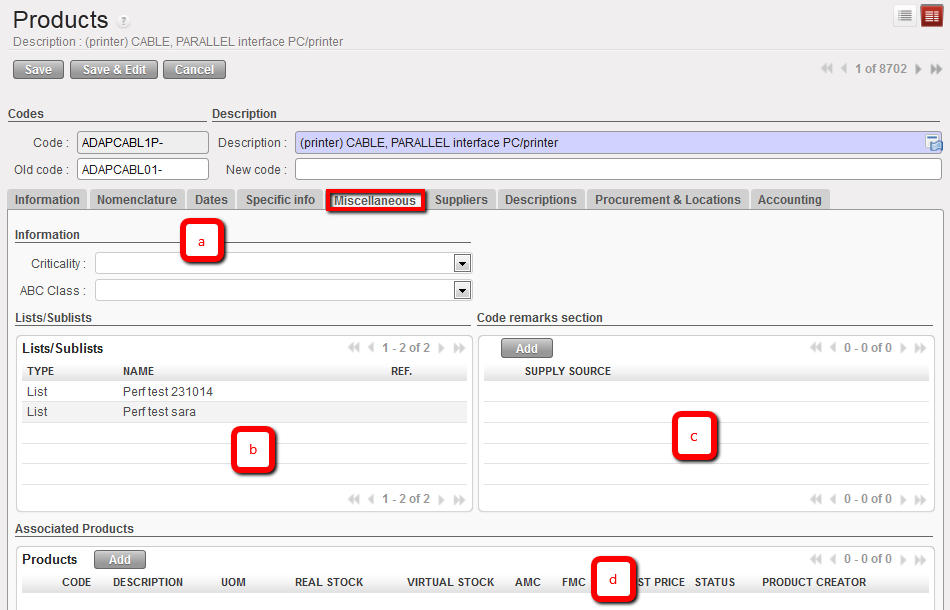
Product Miscellaneous tab
7. Suppliers tab
This tab will display the details of any qualified and approved Suppliers which are linked to this product because: 1) they have listed the product in their catalogue price list, 2) they have been used previously for supplying this product, or 3) because we know the price they have quoted for this product. The Sequence number indicates a quality rating: the lower the choice number, the better the rating, so “1st Choice” is considered a better supplier than “2nd choice”. This field can also be entered manually. The lead times which the supplier requires to supply the product should also be here.
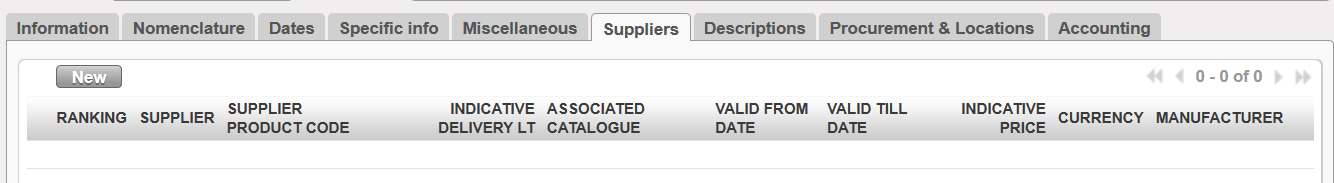
Product supplier information
 Please note: Listing the supplier in this section will give an impact on the system’s ability to facilitate autonomous processes such as PO creation for this product. If the replenishment rules have been set and PO creation (batch configuration) settings have been configured for this product, it is necessary for the product to have a lead time, either that of an associated supplier, or, if no supplier has been associated with it, then a general lead time should be entered for the product in the Procurement & Locations tab.
Please note: Listing the supplier in this section will give an impact on the system’s ability to facilitate autonomous processes such as PO creation for this product. If the replenishment rules have been set and PO creation (batch configuration) settings have been configured for this product, it is necessary for the product to have a lead time, either that of an associated supplier, or, if no supplier has been associated with it, then a general lead time should be entered for the product in the Procurement & Locations tab.
8. Descriptions tab
Product Description
Product catalogue page: to indicate if there is a technical sheet in the catalogue for this product.
Product Catalogue Path: to indicate pathway to any specific documents.
3. Field Description
Description, for product description (this will partially be added by ITC, it can be added locally).
4. Purchase Description
Any text here will appear on the Purchase Order
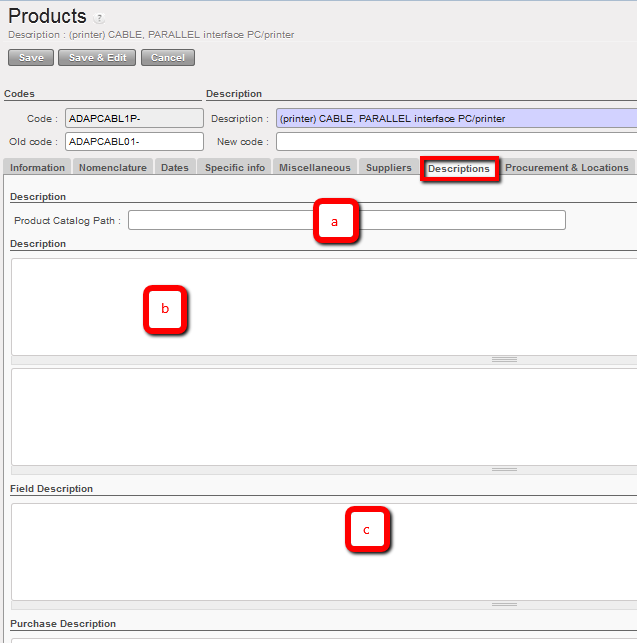
Product Descriptions
9. Procurement & Locations tab
Delays / Lead times Section
Procurement Lead Time is 60 days by default. If there is no supplier associated to this product, then the system will use the value here to calculate any replenishment orders if this setting has been used, so please adjust accordingly.
3. Counter-Part Locations Properties Section
- Procurement Location, the source location generated for a procurement stock move (the system will create this)
- Production Location, as per Procurement Location but for Production
- Inventory Location, as above but when you carry out a physical stock inventory (count).
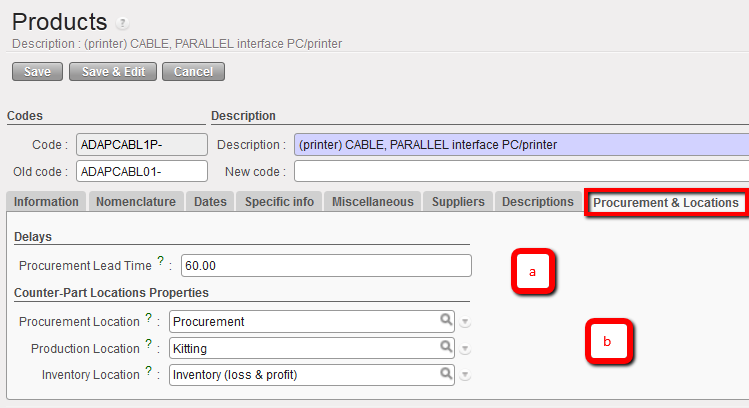
Product procurement & locations tab
10. Accounting tab
The Accounting tab is completed by Finance to tie up a product to a VAT code if the mission is based in a country where VAT can be recovered.
The only mandatory field Supply must fill in is “Inventory Valuation”, for which the option Periodical (Manual) should always be set. All the other fields in the Product form’s Accounting tab are optional as most of finance information will be set by default according to the Product category.
All information entered in the Product form Accounts tab will take precedence over the information in the Product Category (this is in the Information tab, which pulls from the Family classification selected in the Nomenclature tab).
- Stock Input Account = NA for the time being (will be the stock variation account when unallocated stocks option is available)
- Stock Output Account = NA for the time being (will be the stock variation account when unallocated stocks option is available).
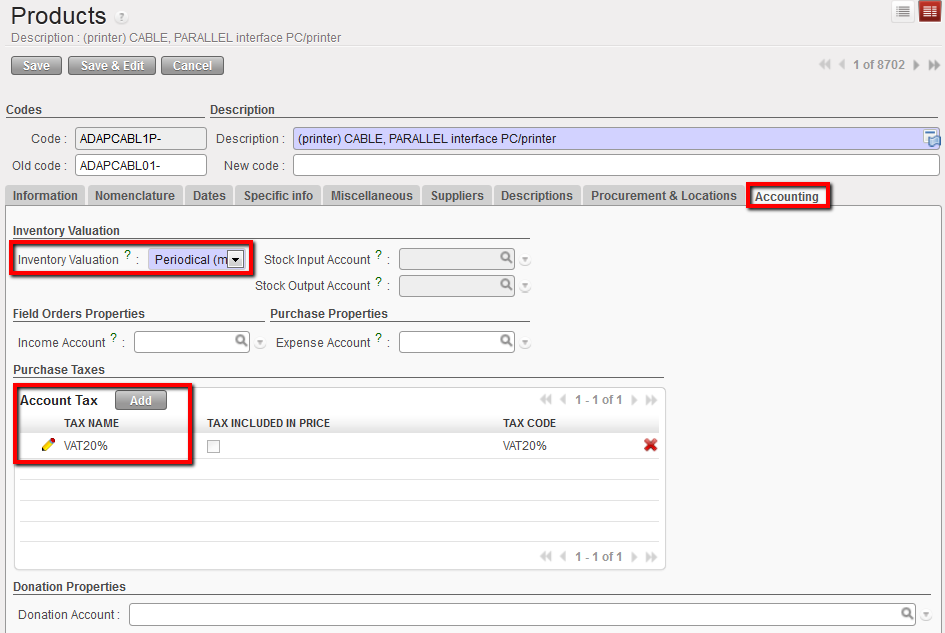
Product linked to a VAT code displayed in the Accounting tab
