Supply User Manual ENG-> Supply Configurations-> 2.1 LU-SU1101: Instance set-up-> C. LU-SU1101: Default Locations
C. LU-SU1101: Default Locations
The structure of locations within UniField facilitates the organization of stocks and also supports the double entry principle, which is explained in details in the Warehouse chapter. Any stackable products received will be part of the internal inventory until they are issued to an external party at which point, they will be removed from any internal locations and will exit UniField. Products which are non-stockable or services with reception will not figure in internal locations but will be received in specific virtual locations. The exception is where non-stockable products are in transit to another internal partner (e.g. project), in which case they will transit through the (coordination) Cross docking location before to be dispatched.
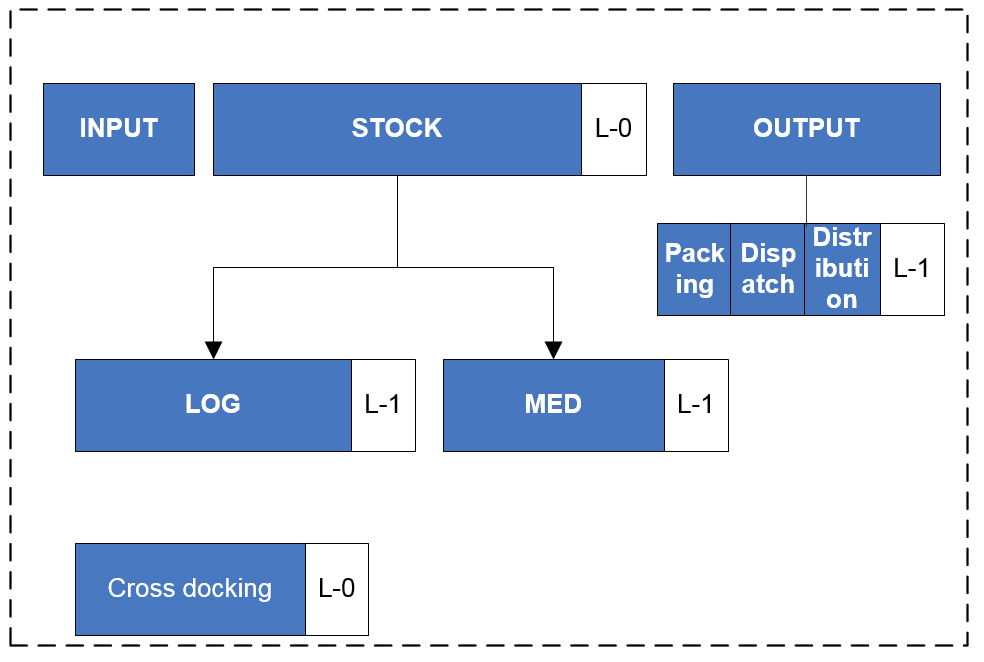
A warehouse in UniField is an entity which represents one or more physical storage locations from a project/coordination office. This warehouse includes a “point of entry” of goods (destination of most of POs) and a “point of exit” of goods intended for a customer (through an FO). Each instance has a warehouse created by default at the instance creation. The warehouse is divided into 4 main parts: Input, Stock (with children locations), Cross docking and Output (also with children locations).
 |
| Instance Warehouse |
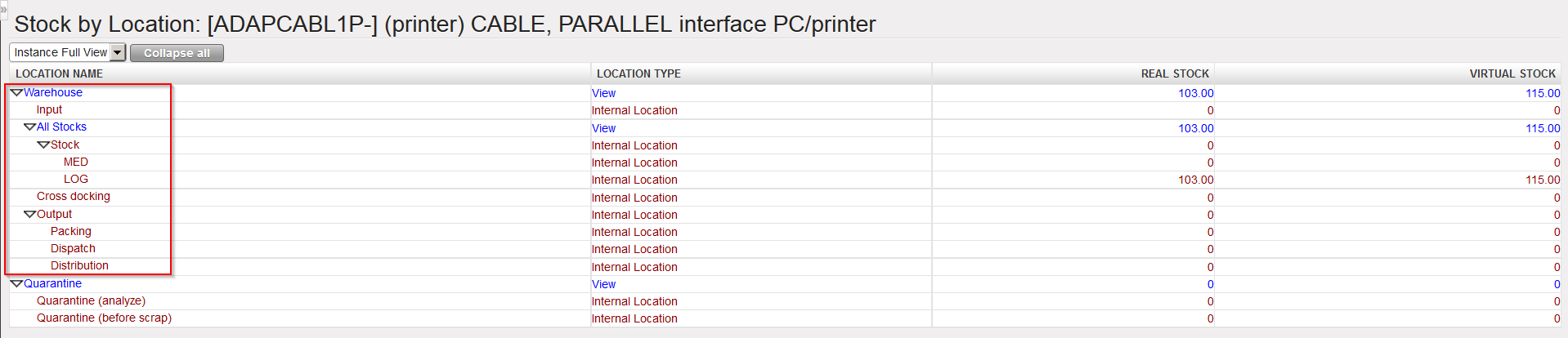 |
| Instance Warehouse (minimal set-up) |
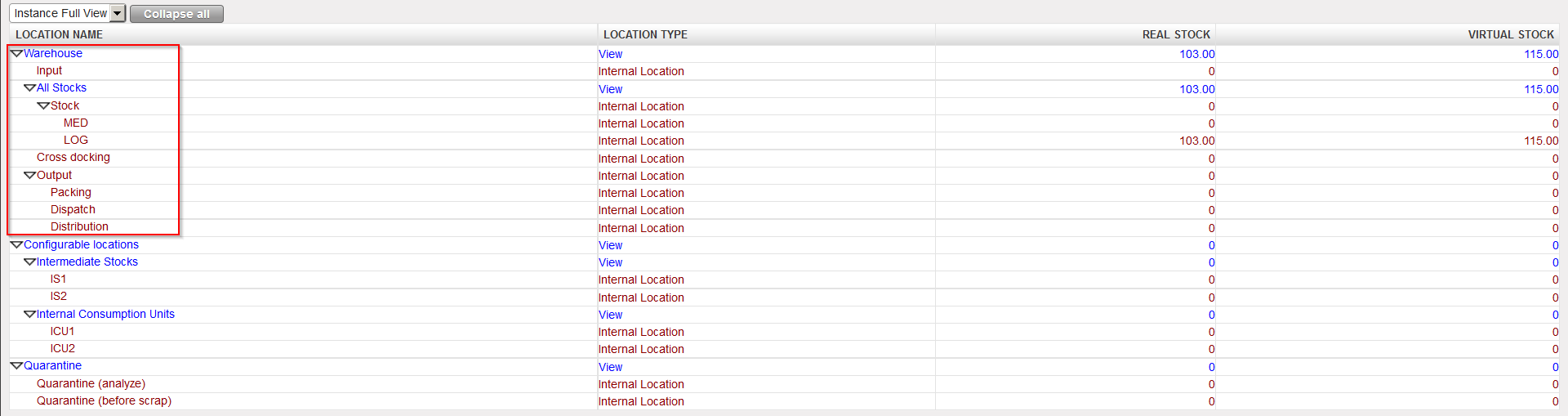 |
| Instance warehouse (including examples of configurable locations) |
Input is a transition location through which received products transit (and where a quantitative/qualitative check can be performed) before being available in stock. It is the destination location of an Incoming Shipment/Purchase Order which is not received in cross-docking.
Stock reflects the main stock from a coordination/project. This location has 2 children location, MED for the storage of medical items and LOG for the storage of logistical items. MED products are stored in the MED location. LOG products are stored in the LOG location. LIB products are stored directly in the Stock location (if they are declared as stockable products).
When an Incoming Shipment (IN) is processed and goods are received in the Input location, the system creates an Internal Move (INT) to transfer the goods from the Input location to the stock. This Internal Move is processed automatically if the goods are received directly in the requesting location (checkbox “Direct to Requesting location” ticked when IN processed) or manually if the goods actually transit through Input for quantitative/qualitative control (checkbox “Direct to Requesting Location” unticked when IN processed).
Goods present in Stock or children (MED/LOG) are considered as available (unless reserved) for any request.
Output is a transition location through which products being distributed to customers transit when the full shipment process (pick/pack/ship) is used. The Output location itself is not used but goods transit through its children locations (Packing/Dispatch/Distribution) during picking/packing/shipment.
Cross docking is a transition location through which received products transit when they are received on an instance but should be dispatched to a customer. An Incoming Shipment/Purchase Order linked to a Field Order has Cross docking as default destination location. An Incoming Shipment/Purchase Order linked to an Internal Request (whose Location Requestor is an External Consumption Unit) has Cross docking as destination location.
