2. Products
Menu Mapping: Products > Products
Preceding documents
N/A
Successive documents
N/A
For Supply, products are the key master data and are used in all Supply objects in each flow.
The right to create and modify products in UniField is restricted according to user rights and type of product (product creator) at different levels. Generally most products should be created in UniField via the interface from UniData. UniData is the master data management system used by MSF movement for managing products in general and their status in particular. UniData sends to UniField all updates regarding products and their statuses through an interface called the Linkage.
Each OC can modify their products before products are loaded into Unifield via UniData. Only product that are OC subscribed and with a “Valid” status will be created and sent to UF. The linkage between UD and UF also enables the updates of products attributes, statuses and de/activation. These products will be loaded to UF HQ, and then will be synched down to all Coordinations and projects of that OC. For other products (local), these can still be created at Coordination and will be synched to that mission’s project (downward synch). However, transition has been initiated so that all local products (NSL) can now be managed via Unidata and HQ, hence reflecting the long term goal. The Field Access Rules (one of group of files considered collectively as User Rights) defines which product fields are created and updated by synch, and which ones can be modified manually.
Different attributes affect the way the products are managed by transactions in the system.
Attributes in product data sheet which affect system treatment, or are impacted are as follows:
Product Code – this has been left flexible for user to create (or to be created via import), so it is not limited / structured according to nomenclatures. This is consistent with original agreement and Unidata principals. Unidata provides guidelines on how to structure code creation. One recent exception has been added with the obligation to have a “Z” in the local product code name created in UF.
In order to facilitate the work on product codes by Unidata (matching and de-duping also called “écrasement”) an extra “hidden” product code has been developed in Unifield to act as a unique identifier for each product – this is the XML_ID code. This code is created for each product at point of creation. By default, it will take the same code as the product code (which is visible in the Product Code field). However, the product code can be changed and updated, but the XML_ID code will always stay the same and cannot be created in duplicate. It is never visible to users except in the files for importing or updating products. It is for Unidata together with OCs to define how this process will work, and which Unifield fields in the product data sheet should be used to facilitate process (e.g. fields Old code and new code, product status, Form Fit & function etc).
2.1 Types of Product
Stockable product, product can be purchased, managed in stock and dispatched for duration of supply chain. If product is Stockable then Product Sub Type must also be selected.
Non-stockable products can be purchased but stock management is limited. If received into IN originating from PO or Internal Request, products will be directed by default into the virtual non-stockable location. For products ordered as part of a synch flow (FO – PO), the goods will by default be received into the cross-docking location and can be dispatched as per the OUT / PICK /PACK /SHIP process, but when received in the consignee instance, will be directed to default non-stockable location (as above). Other warehouse stock management tools such as inventories, internal moves, consumption, reports etc will not be applicable for these products.
Service with reception, as per non-stockable products, these can be purchased but not managed using Unifield stock transactions and tools. At Incoming Shipment, product is directed towards service virtual location. It is not possible to receive service products into Cross-Docking location. For Service products ordered via FO/PO flow (including via RFQ/Tender), PO generated will be type Direct Purchase Order (check done at OST level or when generated from RFQ/Tender which was from FO). Products which are designated as services can also have checkbox “transport” ticked, and when this product is present in POs, this cost will be considered in the Local Transport costs report.
2.2 Product Sub Type
Field & options will appear if Product type has been selected as stockable
Single item, standard sub type.
Kit/Module, can be treated as single item, but in addition, kit functionalities are available (non-mandatory) – Kitting order, Theoretical Composition list, Kit Composition list, etc…
Asset can be treated as a single item but system will require additional information. Asset functionalities are mandatory in some transactions when product managed / moved. This does not affect purchasing stages, but as soon as Incoming Shipment is processed, and for many warehouse transactions after, further information (Asset Form) must be added. An asset form is to be completed for Asset reference to be generated, and this reference is mandatory for Incoming Shipments, Consumption reports, Pick/ Pack/Ship and OUTs. However it is not mandatory for Initial Stock Inventory, Physical inventory or Internal moves. Identification of asset products with mandatory Asset reference is only enforced for transactions where products are entering or leaving the instance, not for internal movements. If sub type of asset is selected in product data sheet, new field Asset type appears and must be filled.
2.3 Costing Method
– Average Price: (this option should always be chosen). This is calculated from the Moving Average Cost of a product and displayed in “Cost Price” field. This means the price will be updated at every reception of the product. The price will not change when product leaves the instance. This price will be automatically populated every time the price is displayed for a newly added product (e.g. IRs, FOs, and for POs this will be displayed except if there is an active supplier catalogue for the product and supplier), and of course this price can be modified. Also described as Average cost price. The price is not updated by the synchronisation engine after the first synchronisation. Each instance can have a different price for the same product.
Product price history can be monitored using the “Track changes – product prices” from the Product action menu. This export is updated at creation/ import of product; Initial Stock Inventory; IN received or following Cost re-valuation.
– Standard Price: this option indicates that the price of the product is fixed and doesn’t change. It means that the cost value of products in stock, and those procured over time will always be the same. This option should not be used, as agreed, but is not blocked.
2.4 Product Creator
This indicates who created the product. Certain rules will be applied according to this.
UniData – synchronised down to COO and Projects via HQ after OC subscription in UniData. Cannot be created at Coordo level or below. To be imported and updated via Unidata/UF linkage, with OC input.
ITC – UniData product ancestor – should not be created anymore even though some ITC products may remain despite cleaning (used to be common to all HQs and missions). Most of these products have been updated to UD or “écrasé”.
ESC – UniData product ancestor specific to ESCs – should not be created anymore even though some ESC products may remain despite cleaning (used to be common to all HQs and missions who use the ESC). Most of these products have been updated to UD or “écrasé”.
HQ – UniData product ancestor specific to HQs – should not be created anymore even though some HQ products may remain despite cleaning (used to be specific to HQs). Most of these products have been updated to UD or “écrasé”. They are now specifically subscribed by one OC from UD.
Local – UniData with Standardization level NSL (Non Standard Local) product ancestors. Should not be created anymore (Used to be created in Coordination instance and synchronised within the mission – down to projects) but still technically feasible providing the right User Rights. Some of these products may remain despite cleaning done by merging (see §2.2.7 below). This product cannot be ordered from or to Intersectional partners.
Temporary – only synchronised within the instance
No product should be created at Coordination (not anymore) or project level.
2.5 Standardization Level
This indicates the nature of the product. Certain rules will be applied according to this.
Standard – product used and validated by all OCs
Non Standard – product used and validated only by certain OCs
Non Standard Local – mission specific products that can be used by several OCs
2.6 Active and de-activation of products
The active checkbox will be by default ticked at creation of product and means product can be used and managed in system.
A product can be de-activated by clicking the De-activate product button, which will trigger the system to check if product is present in stock or any open orders. If one of these is the case, the system will show in pop up window which or both, and if in open documents, the reference of the documents will be displayed. If cross check is successful, product will be de-activated
Another way to deactivate a product is via the UD Linkage: product will automatically be de-activated following an update from UD. In case the product is Unsubscribed in UD or has status “Archived” the “UF Status” will be updated to “Archived” and Deactivated in case there is no Stock nor pipeline in the HQ Mission Stock Report (MSR).
However, in case there is still stock or pipeline in the MSR, the checks will lead to a product “Not Run update” with a clear message as why the product has not been de-activated. Product will remain Active with a “Phase out” status until there is no more stock or pipeline. A scheduler ( set in “Administration> Configuration> Scheduled actions> HQ deactivate UD products” in UF) will check regularly at HQ level that there are no more product in stock or pipe and then will de-activate the product in HQ and synchronize to all missions.
Please note that in case there are still open documents at mission level, the product will not be deactivated and a clear NR update message will inform user (at mission level) that product could not be deactivated because of open document. User will have to clean the issue and then deactivate the product manually.
In case of synched flows between Instances with different products (e.g. Intermission or Intersection), when PO or FO is created by synch and includes a product which does not exist in the receiving instance, there is now a message onscreen on the relevant document (PO or FO) a clear Not Run message created, warning the user that a product code could not be created.
Deactivation is not a final step and can be reversed (except for Local UF products, Z code, which are inactivated automatically after merged with a UniData product – one shot). Inactive products cannot be added to transactions. Inactive products will be hidden when searched for from transactions, and in order to see them, the filter button ”Active” must be cleared while “Inactive” will be toggled on.
Tools > Product Status Inconsistencies (US-1167)
This report is only meant to be generated at HQ and COO (US-6796).
This report has been developed to identify any inconsistency when launched on HQ instance compared to COO (while launch on COO will raise inconsistencies between COO and projects). It is comparing UniField status/UniData status/active-inactive status of products present on HQ with the statuses of these products on the various coordination instances. If a difference is spotted, the product is displayed in the report.( e.g. A product is active at HQ but inactive at COO).
The number of project instances linked to the COO is limited to 10 for display purposes.
Please note that given recent synchronisation rules and the UniData Linkage these inconsistencies should not happen as often.
2.7 Product merge (US-7353)
Merging Local product (Z code) to Non Local Standard products at UF Level
This specific function has been developed in UniField to smooth the transition of management of Local product from UF(Z code) to UD. While local products used to be created and managed at mission level by Coordination in UF there are now created and managed from HQ level via UD. Creation and update will be synchronized down from HQ to the missions.
Merge of a local UF product to a UD product is a one-shot action that can only be done on a one to one basis. The “Merge” button is only displayed on UF local product (Z product) at Coordination only.
Please note that the UD product to be merged can be Standard, Non-Standard or Non-Standard Local (NSL). The NSL products are synchronized down from HQ to Missions as inactive.
Merging with NSL UD products can only be done on inactive and never activated NSL products. Therefore, the default display of product to be merged will list all NSL inactive products.
In order to display the Standard and Non-Standard UD products, a checkbox will need to be ticked. Then the list of all active Standard and NS UD products will be selected.
In addition to this filter, some checks will be done so that UD products should not have any history or presence in a Mission Stock Report. A clear blocking message will be raised in that case.
A blocking warning message will also be raised if the products have differences regarding the following attributes: Expiry Date Mandatory; Batch Number Mandatory; Type, Sub-Type and Default Unit of Measure. This message will urge user to update the attribute on the Local UF product. Non-blocking message will be raised for discrepancies between these attributes: Main type or Temperature sensitive. Any other discrepancies on other attributes will be overwritten with the attributes of the UD product.
Upon merging, the UF local product is deactivated and all its historic data is merged to the new UD product meaning that the code of the new active UD product will replace the old UF product on all existing open and closed documents. Therefore, the only trace left of the UF local product will be in the “Old code” field (and track changes) and in Old Products Field in any Products lists where the product is existed.
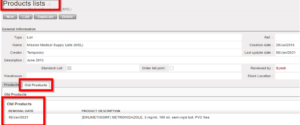
Merging done in Coordination will be automatically synchronized down to the project’s mission. Not Run messages can be created in case discrepancies exist between project and Coordination (i.e: product exists on an open transaction at project).
2.8 Stocks section
Stock quantities are calculated by the system and cannot be edited. These fields in the product data sheet only calculate and display quantities for products in the main warehouse, so configurable locations are not taken into account.
Real Stock: quantity computed in real stock (LOG and MED)
Virtual Stock: quantity computed in virtual stock (and children) (see section on Virtual stocks/products for more information on this)
Monthly consumption: view of stock consumed (or which has left the system) for one month during the past 3 months
Forecasted Monthly Consumption: This is the estimation of the quantity of the product which will be consumed over a month. This information is calculated according to the monthly consumption report
2.9 Expiry Date Mandatory:
Where this is activated in product data sheet, this information must be recorded manually at the time of arrival of the product(s) in the system. This information will then be mandatory for all stock management transactions until the product leaves the system. For products which are only Expiry Date mandatory (and not Batch number mandatory) at the point of selecting an expiry date, an internal batch number form will automatically be created with a sequential reference MSFBN/XXXXX which will be linked to the batch reference and the product, and this Batch number data sheet becomes system master data.
2.10 Batch numbers
Where checkbox “Batch Number Mandatory” is ticked, the Expiry Date mandatory checkbox will also be ticked automatically (i.e.: a product flagged with BN mandatory should always be flagged ED mandatory as well). When a product is first received into the warehouse module of the system (e.g. via incoming shipment or initial inventory), this information will be mandatory for every stock management transaction until the product leaves the system. The Batch number given will be linked to the selected expiry date and the product and saved as a Batch number data sheet as part of the system’s master data.
Both Batch number data sheets (BN & ED) will accompany products which are BN/ED if they are sent via a Delivery Order or Shipment to another internal instance via synch, and consequently will also be created in receiving instance.
Product BN/ED Mass update (US-6468)
This functionality enables to update BN/ED product attributes from HQ and sync’ their information down. This feature can be used for a minimum of 2 products.
When changing Non BN/ED products to BN/ED product, the products already in use at mission level will have their value updated to “BN = TO-BE-REPLACED” and “ED = 31/12/2999” on all existing documents and Stock. It is recommended that these default values should be manually changed later by the users.
For the other way around, where products “lose” these attributes, the BN/ED information will simply be deleted and products quantities aggregated in Stock.
For ED Product moving to BN/ED, the BN reference will be switched to “TO-BE-REPLACED” while if product moves from BN/ED to ED only then the BN reference will be an internal one (MSFBN/XXXXX)
Tools >Product Inconsistencies report (US-279)
This report has been developed in the past to help identify any BN/ED vs non BN/ED product inconsistencies (i.e.: a BN/ED product is missing BN/ED information or a non BN/ED products actually has a BN and an ED) However, since last development with Product BN/ED mass update these inconsistencies should not happen anymore since document and stock are automatically updated (see paragraph above).
2.11 Short Shelf Life
(check box in the “Dates” tab), if this is ticked in a product, when this product is ordered (PO/FO), the system will alert user with top of screen message that accuracy should be checked. If Short Shelf life checkbox is ticked then Product Life Time field will be active. Product Use Time if entered should be less than the Product Life time.
Product Alert time is a period of time set for a product when, if it is in stock, the system will alert user about this batch / group of products.
2.12 Temperature Sensitive
Items (“Specific info” tab), where products are indicated as Thermosensitive item or cold chain
2.2.13 Controlled substance
This (dropdown list in “Specific info” tab), if active will be shown as ticked in warehouse transactions (IN, OUT etc).
Dangerous Goods (dropdown list in “Specific info” tab): If active will be shown as ticked in warehouse transactions (IN, OUT etc).
2.2.14 Restricted in the Country
(checkbox in “Specific info” tab) if this is active then Country Restriction can be selected from master data of Country restrictions activated if the instance has been configured with one or more restrictions
2.2.15 Form, Fit & Function fields (“Specific info” tab)
These fields were added on request of the Unidata/Codification project. They have no technical or functional impact on other transactions. The original value will be synched with the product as will any update (as per synch rules in IT documentation).
2.2.16 Lists/ Sublists section (“Miscellaneous” tab)
This field will indicate all lists and sublists where the product appears.
2.2.17 Suppliers tab
Suppliers may be added to a product datasheet because: 1) Supplier has Supplier Catalogue for this product 2) Supplier has been selected in a Tender for this product or 3) because supplier has been added manually. The Sequence number indicates a rating: the lower the number, the better the rating, so “1” is considered a better supplier than “2” and “-1” is better than “1”. When a supplier has been selected to supply a product via a tender process, the supplier will automatically be added to the product sheet with the ranking of -99. If a Supplier is added due to having a catalogue with this product, the sequence will be 0. All sequences can be changed manually. The lowest sequence value will become the preferred supplier for all sourcing in the Order Sourcing Tool and will be the default supplier for POs created due to Replenishment rules. (Bug here – US-420)
Counter-Part Locations Properties Section – see section on locations (Internal, virtual and partner) for more information on this concept.
2.2.18 Accounting tab
The Accounting tab is relevant to the Finance domain. Please see Finance documentation for information on this.
All information entered in the Product data sheet, in the Accounts tab will take precedence over the information in the Product Category (this is in the Information tab, which pulls from the Family classification selected in the Nomenclature tab).
2.2.19 Product Mass Update
Products > Product Mass Update (US-1080)
Most of the products attributes mentioned above can be updated by mass. Even Activation and Status of products can be managed for several products at once from HQ via an import file.
Please note that mass update will apply the same type of updates to several products ( for example, update them all to the same status – you cannot update some products to a status and some with another one; you will have to perform another mass update for the other status).
2.3 Product Status and Linkage with UniData (US-7158)
2.3.1 Product Status (UD)
Menu Mapping: Supply Configuration > Product > Status
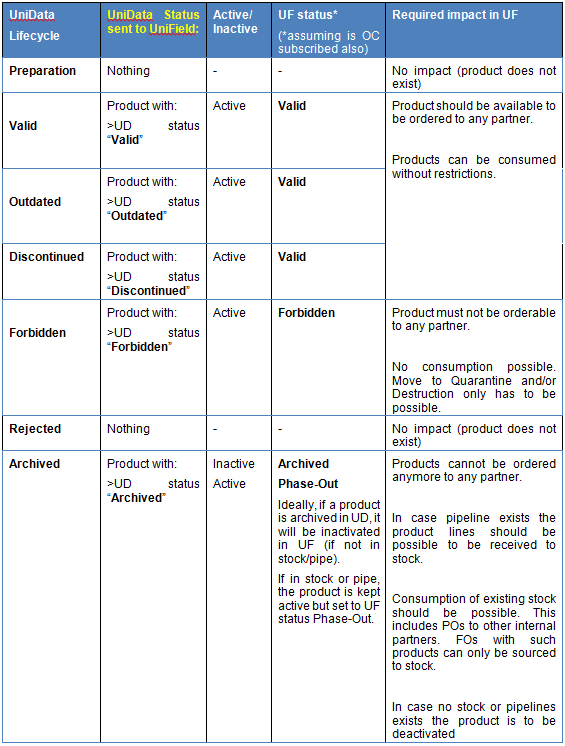
As mentioned above, the UniData Linkage is playing a huge role in the product status maintenance. While historically the UD status used to have no impact on the UF status, the last developments changed this behaviour: updates of statuses coming from UD are now triggering UF statuses updates.
In the Product Master Data sheet, user can still see 2 distinct fields to differentiate these statuses: “UniField Status” vs “UniData status”.
The “UD Status” will be automatically populated with information coming from the Linkage to UF HQ instance. This update of the “UD Status” will trigger the update of the “UF Status” thanks to a pre-established mapping table ( see below) and will then be synchronized down to UF Missions. These fields will therefore not be editable for UD products.
The “UF Status” remains the one with a direct functional impact in UF product usability (i.e.: for instance depending on their status some products can still be ordered or not). Mapping table below will also present the status impact.
There are now 4 “UF status” while UD presents 7 statuses:
UF status: Valid, Phase Out, Archived and Forbidden
- Valid – Can be used as a normal product; can be ordered, stocked and consumed (Active)
- Phase Out – Can be stocked and consumed normally, but ordering is limited to only internal partners (i.e: excluding as well ESCs) (Active)
- Archived – cannot be ordered, stocked or consumed (Inactive)
- Forbidden – cannot be ordered, stocked or consumed in the field. To move to quarantine/Destruction (or Internal FO from Stock) (Active)
UD status: Preparation, Valid, Out dated, Discontinued, Forbidden, Rejected and Archived.
- Preparation – Article proposed being discussed, tested or considered
- Valid – MED: Article is validated according to medical framework
LOG: Article is validated based on the 3F+ details, may be used Archived – cannot be ordered, stocked or consumed (Inactive) - Outdated – Can still be used, but either the need has evolved , or there is a replacement, or it is not commercially available anymore
- Discontinued – Outdated at least 3 Years, Can still be used.
- Forbidden – Forbidden to be used in the field
- Rejected – Preparation article that was never validated for use
- Archived – Not used, can be reactivated
Each of the active statuses can be applied to any product and will affect how the product can be used in the system. The status names were updated in accordance with request for more consistency with Unidata statuses.
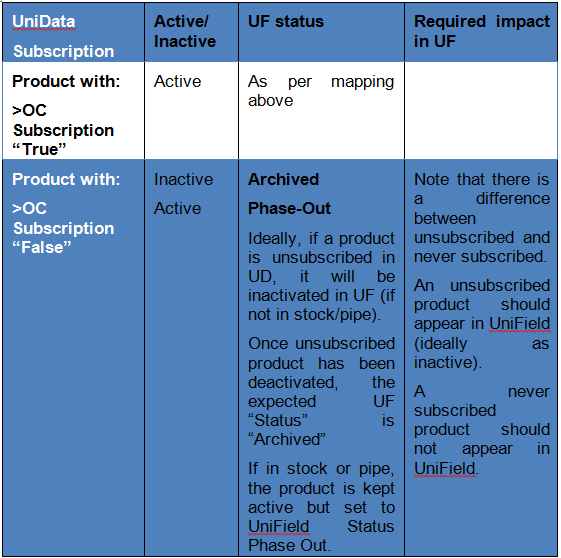
2.3.2 OC Subscription/ Unsubscription
Menu Mapping: Supply Configuration > Product > OC Subscription
UniField products with “Creator” = UniData need to be first OC subscribed at UD level before being created. Only these products will be sent from UD to UF via the Linkage and therefore created in UniField.
2.3.3 Merging UniData products at UD level
UniData can take the decision that multiple existing UniData products actually only match with 1 product, and therefore there is a decision to “merge” these products so that only one is considered the “true” valid product. This “valid” product might need a new code and description (écrasement).
If the affected products exist in UniField, the following happens:
- UniData contacts the OC to raise the necessary “merge” with listed duplicate products via a multiple truth message (e-mail) sent to the OC focal point.
- OC checks if these products are in stock / open transactions / Product list and communicates this to UniData. Then:
- The code, description and other attributes of 1 of the products are updated by UniData. The code remains active and valid in UniField (“écrasement”). UniData fills attribute “Old Code” with the codes of all Products affected by the merge.
- The other products affected by the product merge need to be deactivated (or phased out if there is still stock, open document or pipeline). The attribute “New Code” contains the code of the merged Product.
In the case the un-necessary code/s is not in stock, in pipeline or in a product list, the UniField mechanism is able to deactivate the code.
Some limits of this process have been raised (US-8055):in case one of the old product is Phased out (because of Stock, pipeline,…) then the merge still cannot be done since there should only stay one product Valid and Active the other product need to be Inactive (not phased out active).
If user tries to add / manage product in forbidden action, system will display warning and block action (e.g if user tries to source product with “phase out” status to external supplier, system will display message and prevent sourcing.)
Products with no status will be treated as valid, however this situation should no longer exist with UD linkage (all UF status = empty should have been updated to Valid)
Searching for documents for specific Product:
In the Products/PMD Action menu, there are links to see the relevant documents for selected (ticked) product. Links are displayed: Field Orders – Internal Requests – Purchases- RfQ’s – Tenders – Incoming Shipments – Internal Moves – Delivery Orders – Picking – Packing.
Menu Mapping: Tools > Export Stopped Products (US-1671) (name will probably be changed to “Export Phase Out products” with US-8067)
A report has been developed to spot all products with “Stopped” (Phase out) status that are still in Stock or in the pipeline in order to identify them per instance and help with an expected cleaning.
Following linkage with UniData, this “Stopped” status is not meant to exist anymore and should have been replaced by “Phase Out”.
This report is to be generated only at HQ level.
This report in excel will display all products where the UniField status in an instance = Stopped (Phase Out) AND there is either a qty in stock OR qty in the pipeline.
If there is no instance for which product meets both these criteria, only header should be displayed (i.e.: product is only “Stopped” Phase Out at HQ)
For Qty in stock or in pipeline any qty <>0 will be considered.
If in an instance product UF status is “Stopped” (Phase Out) but the Qty in stock and in pipeline is 0 then this will NOT be displayed.
The system will only show on an instance basis where both of these conditions are met.
The system is not expected to calculate / filter anything according to “UniData status” of product.
2.4 Units of Measure
UniField supports several Units of Measure (UoM). The same product can be expressed in different units of measure. All the units of measure used for a product must be in the same UoM category. It is not possible to convert something which has a UoM of Kg into cm as these 2 UoMs belong to different categories. If a product has a UoM which belongs to a weight category, it can only be converted into another weight category UoM. Once a product has been saved with a certain UoM (default and exchangeable) it will no longer be possible to change it to a UoM of a different category.
Samples of Units of Measure (UoM)
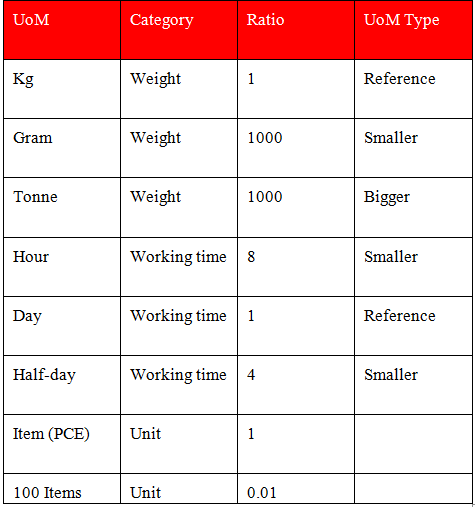
Units of measure selected in the product data sheet are pulled from Units of Measure master data. In the definition of a Unit of Measure, there is a “rounding precision factor” which shows how amounts are rounded up or down after the conversion. A value of 1 would be rounded to the level of one unit. 0.01 means the product would be rounded to one hundredth of a unit.
2.5 Nomenclatures
Each product in Unifield will have several levels of nomenclature which act as a classification of the product. The nomenclature levels are type, group, family and root. The system also provides optional levels which are classes. The nomenclatures do not relate to the product code, which was a deliberate decision. The family level of nomenclature chosen for a product is directly linked and displayed in the Product data sheet “Category” field also. This has an impact on the expense / income accounts in Finance, and so also affects the Analytical Distribution Destination associated with this product. See Finance document for more details on this.
The nomenclature creation and management is done at UD level upon request from OCs. Note that Nomenclature level can help define which products are BN or ED mandatory.
Where a product code is not known or does not exist for a product which needs to be requested/ordered, it is possible to create an order for a “product by nomenclature” which means selecting the 4 levels of nomenclature to define the product. This is possible in Internal Requests, Purchase Orders and Field Orders.
The “Main Type” : MED, LOG or Service will determine where the products will be received when the default location is “Stock”.
2.6 Product lists
Product lists & sub lists are not part of Supply order flow, but product lists can be used to select/add products to the following objects via the add multiple button. In addition if not all products of a list will be needed, surplus products can be deleted via delete products button functionality.
1)Product list
2)Product sub list
3) Theoretical kit composition
4) PO lines
5)RfQ lines
6)Tender lines
7)Claim Products
8)FO lines
9)IR lines
10)Supplier catalogues lines
11)manual IN lines
12)INT lines
13)manual PICK lines
14)manual Delivery Order lines
15) Replenishment Rules
16)Physical Inventories
17)Initial Stock Inventory
18)Real Consumption Report
19)Monthly Consumption Report
20)Products Situation Report
21)Product Cost revaluation
22)Product Mass update
23)Product BN/ED Mass Update
2.6.1 Types of Product lists
List – List of products not specifically designated for any location, can act as a parent list to one or more sub-lists
Sub-List – can have parent list. If Parent list is attached, products which can be added to Sublist are limited to those in parent list (currently bug US-417)- Sub-list must have warehouse or stock location attached (mandatory).Sub-list can act as parent list to other Sub-lists.
If checkbox “Standard List” is ticked, list will be synchronised down.
Products tab displays products currently in list, and Old products tab shows products which were previously on list but which have been removed, displayed with their removal date.
5.6 Statuses of Product lists N/A
5.8 Updates from successive documents N/A
5.9 Direct Reports / Exports
Product List Excel Export
Product List/Sub List
2.7 Partners – customers, suppliers and manufacturers
Given their very nature, Partners are at the heart of UF as well and are used by Supply as much as by Finance. Therefore, their management needs to be thoroughly coordinated between both departments. (The specifications below are more Supply oriented and can be completed by having a closer look at the Finance specifications)
Partners represent important master data for Supply as they are used in order flows.
Partners can be Internal (within the MSF UniField network) or external (all entities, MSF or not, not on the UniField network). Some Internal Partners will be created automatically via the synchronisation. Some partners created by the synch will need to be activated (active checkbox ticked) or else they will remain hidden from standard list view except if “Show inactive” filter button applied.
2.7.1 Types of partners include:
- Customers (project or any requesting instance – used in FOs)
- Suppliers (any entity internal or external, which supplies the instance with goods – used in POs, RFQs, Tenders)
- Manufacturers can be added to product data sheet in relation to Supplier(s)
- Transporter – a sub-type of supplier, developed primarily to be used in Shipment document to identify carrier.
At partner creation the default values “Customer” and “Supplier” will automatically be flagged (checkboxes ticked).
The type of partner selected will trigger the system to request specific information, and will also impact processes which partners are involved in. A partner can be:
- Internal, MSF entities which are part of UniField network within the same MSF mission (1 Coordo and 1 or more projects) are considered Internal customers/suppliers, and will be created via the synchronisation.
- Intermission, these will already exist, as soon as the new instance has been created (and synchronised) but will need to be activated when needed.
- Intersection, MSF missions belonging to other sections within the UniField network are also considered customers/suppliers. These will need to be created manually, at HQ, but only on a needs basis. It is important to name them in exactly the same way as their instance is named, in order to be recognised by the synchronisation engine.
- External, refers to all suppliers and customers outside of the UniField network. Some may need to be created / imported manually.
- ESC, European Supply Centres such as MSF Logistique and MSF Supply are considered suppliers. They are created in the same way as External partners. And usually should be created at HQ and synched down to Coordo and more recently to project as well (as inactive).
2.7.2 Partner Attributes
A partner can be created manually, via import or via the synch. A partner can have multiple addresses with contact information added. These addresses will be displayed in the relevant documents (PO, FO, Tender, Incoming Shipment, Delivery Order and Shipment). (at shipment level, if the address is different, the main Shipment will be different as well even if the Customer is the same)
To avoid creation of duplicate partners, check is done at partner creation on Name + City. In case the combination Name/City is the same an error message will prevent creation of the new partner.
Checks on partner name also prevent edition/writing on any partner which have a name that already exists in the instance (set as intermission or intersection). However, there are 2 exceptions to this rule: in case the partner name equal to the current instance name or in case the partner is Internal. (US-3166 and US-2014)
Language selected for partner will impact language of document generated for orders – ie Purchase Order sent to Supplier with “French” selected will be in French. Default language is English so this needs to be changed manually if different. All documents related to this partner will be printed in this language. If not, it will default to English.
Zone selected will impact whether PO is considered as National or International. If PO has a Supplier which is international, it will contain extra fields for Transport cost details. Any International transport costs added to POs can be seen via report International transport costs. ESC type Suppliers will have International zone selected by default.
Order creation mode selected will affect how lines which are sourced to the supplier are grouped on the procurement document. Lines will always be grouped onto PO by Supplier and Requested Delivery Date, but there can be additional ways to separate lines according to the Order Creation Mode selected:
-
- All requirements – is default value (except for ESCs). This means all lines from different orders (IRs & FOs including from different projects) will be grouped onto one draft purchase document.
- Requirements by project- is default value for ESCs, and means lines from different project orders will be added to separate draft purchase documents. This option was deemed necessary mainly for ESCs who prefer to receive individual Purchase Orders per project
- Requirements by category – means only lines from orders with the same category (Log, Med, Other etc.) will be grouped onto the same draft purchase document
- Requirements by category and project – means lines from orders with same category and for same project will be grouped together
- Requirements by order – the most restrictive option, meaning only lines from the same order (IR/FO) will be grouped onto the same draft procurement document.
In Categories: It is possible to link a supplier or customer to partner categories. Multiple categories can be selected for the partner. If this field is completed, partner can be retrieved using the Categories filter in the Suppliers Search view.
Purchase and Field Order Default currencies will by default be the Functional Currency. But can be changed for internal instances. For ESCs, these currencies should always be the OC’s functional currency and the system blocks all other currencies.
In any case, both PO and FO default currency need to be the same when saving partner.
Also regarding PO >FO flow, currency needs to be the same between both documents, otherwise a NR will be raised.
Supplier Lead time: By default 0, but can be changed. This will affect all calculations of order lead times for this supplier (orders & replenishment rules)
Catalogues – Any catalogues existing for a Supplier will be displayed with information.
Claims – Any Claims existing for a Supplier or Customer will be displayed
Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable, are, other than the Partner name, the two main fields which are mandatory to be added at partner creation. See Finance for more details of impact on Finance transactions.
Donation payable Account – this field must be filled (mandatory) if Partner is a Supplier which will be involved in In-Kind Donation flows. When created from higher instance, this field will be synchronized down.
Fiscal Position – this field can be filled with taxes status applicable for this Supplier which should link to product (s) see Finance for more detail.
A partner can be de-activated. If the “Active” checkbox is unticked, the system will hide the partner from view, so that it cannot be selected or used in any new transactions. In order for a partner to be de-activated, it should not be actively being used in any open transaction. If the partner is being used in an open transaction, the system will not allow it to be de-activated.
2.8 Supplier Catalogues
Menu mapping: Partners / Suppliers / Supplier Catalogues
The Supplier catalogue functionality is linked to the supplier data sheet and is a list of products with prices and relevant information such as minimum qty. Creation of a Supplier catalogue will by default add the ranking/sequence of 0 to each product’s data sheet for the Supplier concerned. Any product lines sourced via the order sourcing tool to a PO/DPO to this Supplier will automatically take the catalogue price indicated, as long as relevant to ordered quantity. Catalogues can be created at any instance level, and will always be synched down as Active to the lowest level as long as the supplier is Active (for ESC at project level for instance). Catalogues can be updated by the synch (note that catalogue deactivation is also synchronized down). Only one valid catalogue can exist per Supplier for a given time period.
Coordination catalogue will be created at Coordination level and synchronized down to the projects mission but cannot obviously be used as a supplier within Coordination instance itself.
Statuses:
Draft – initial status, all modifications can be made, but catalogue will not be considered active for order process or to be synched.
Completed – catalogue information will actively be used in orders. Manual modifications cannot be made, but those from the synch will be accepted. This status can be reset to draft for all manual changes and then re set to completed.
2.9 Pack Types
Menu mapping: Supply Configuration / Warehouse configuration/ Regular Warehouse Management / Pack Types
Pack types can be created for an instance which can then be used in the PPL as a pack with standardized dimensions.
