Finance User Manual ENG -> 2. Finance Configurations -> 2.4 Financial Accounts.
LUFI-20401 Account Properties
LUFI-20402 Account Inactivation
LUFI-20403 Chart of Financial Accounts
LUFI-20404 Account Mapping
LUFI-20405 Country Code Mapping
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTS
LUFI-20401 Account Properties
LU Introduction
Financial accounts classify, measure and record MSF expenses via the Chart of Accounts. In this LU we explain what the account properties are and how they should be set up in the financial account forms. In order to function well, a financial account needs a proper set up of parameters.

The Account Type defines the account category to which the financial account is related. It defines the nature of accounting entries booked under this account.
Go to Accounting/Configuration/Financial Accounting/Accounts/Account Types
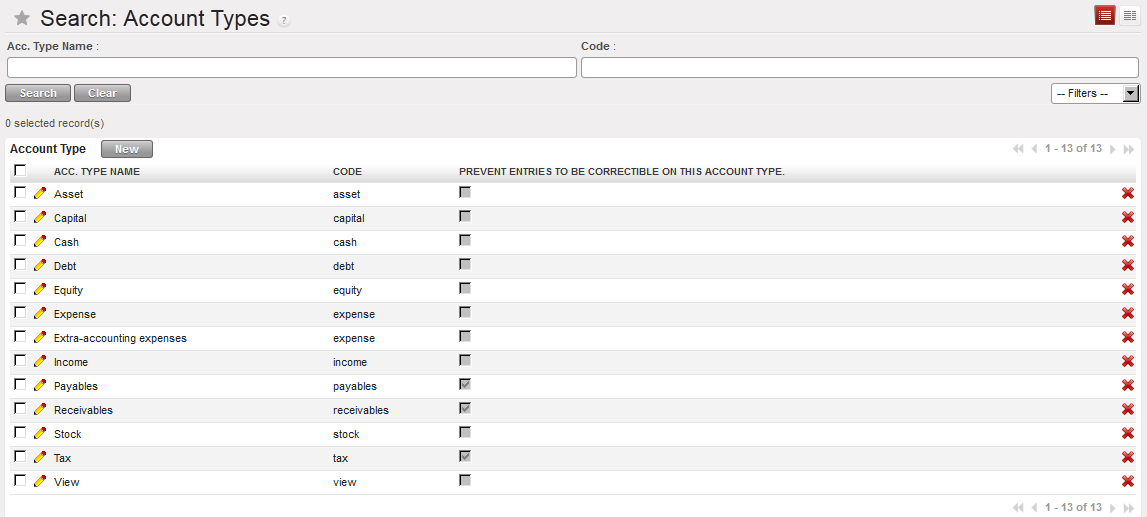
Account Type in UniField displayed in the Search Account Types view
If you want to limit corrections on a specific account type, check the box of the attribute {Prevent Entries To Be Correctible On This Account Type}.
Select the {Edit} button to proceed.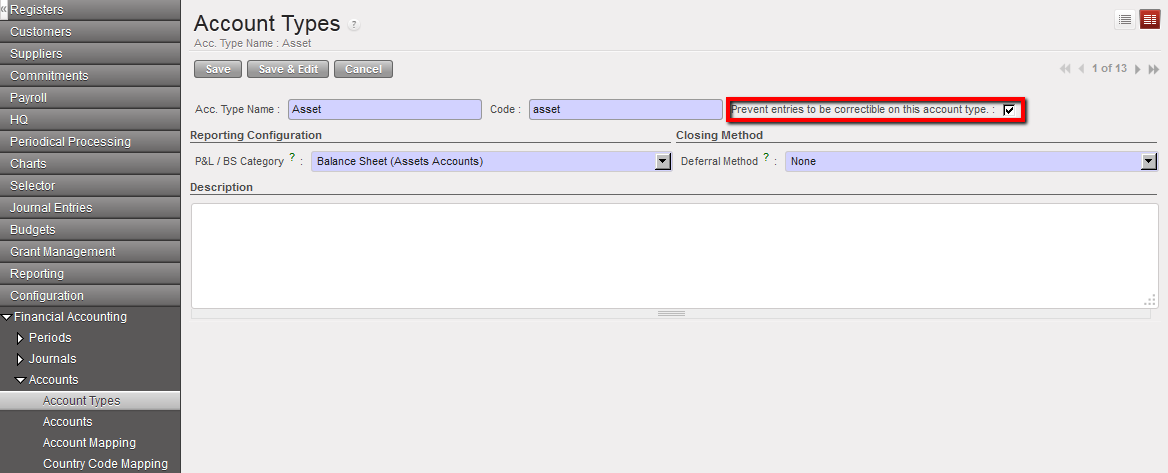 Account type Asset not correctible
Account type Asset not correctible
Each financial account has Attributes or properties. These are:
- Internal type,
- Account type,
- Type for specific treatment,
- Accrual Account,
- Prevent correction on account codes
- Prevent correction on analytic accounts
- Shrink entries for HQ export
- Activation/Inactivation date
- Reconcilable
- Allowed Partner Types
- End-year closing
- Revaluation
Go to Accounting/Configuration/Financial Accounting/Accounts
The account properties can be found on the Account form itself.
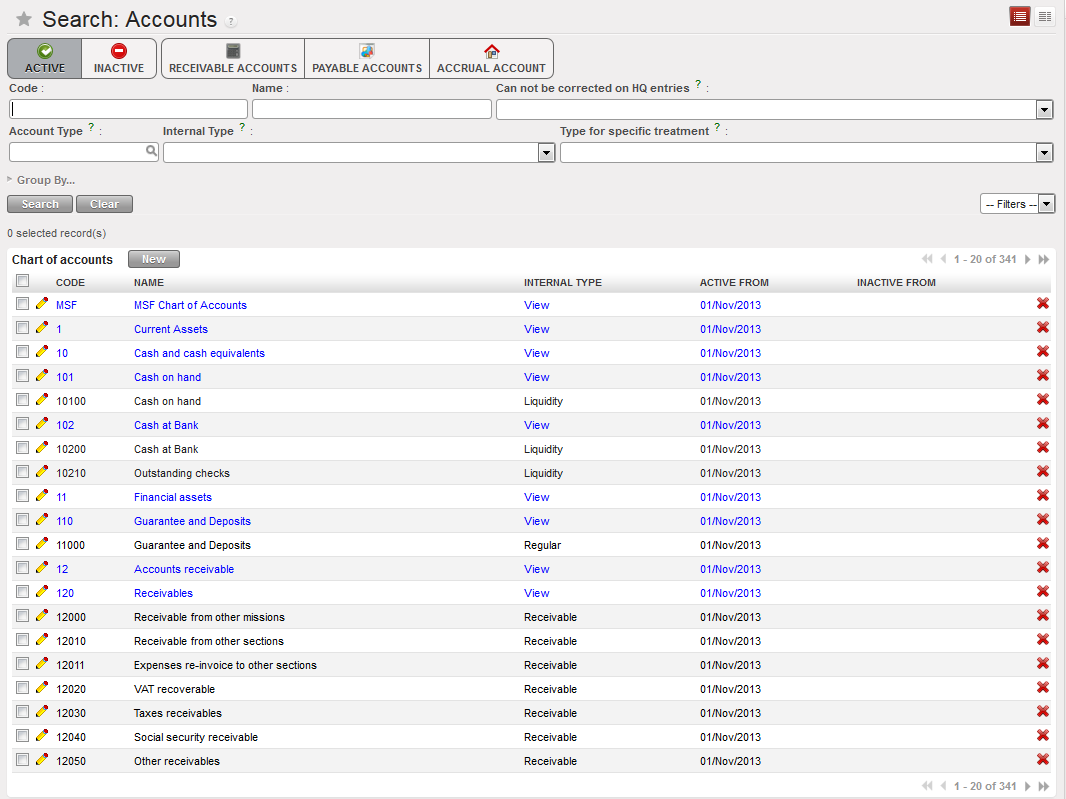 List of Accounts available in the {Search Accounts} view. The view offers a list of buttons to filter the accounts you search. In this view, only the active accounts are displayed as the Active button is checked.
List of Accounts available in the {Search Accounts} view. The view offers a list of buttons to filter the accounts you search. In this view, only the active accounts are displayed as the Active button is checked.
 Select the pencil to open the Account form view to see or edit the account’s properties
Select the pencil to open the Account form view to see or edit the account’s properties
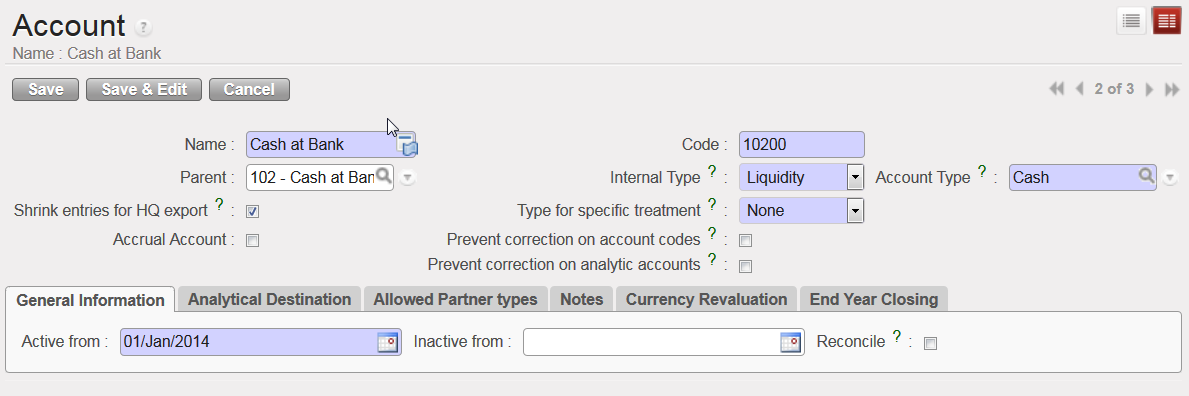 Account form view and corresponding attributes
Account form view and corresponding attributes
The Internal Type specifies the account behaviour:
- A {View} or parent account consolidates the regular (or children) accounts which are linked to it.
- A {Regular} or child account does not have specific properties and is used to post entries.
- {Receivable} and {Payable} accounts are used to book transactions with Third Parties. A third party can be a supplier, employer or a journal and the accounts are defined as {reconcilable}.
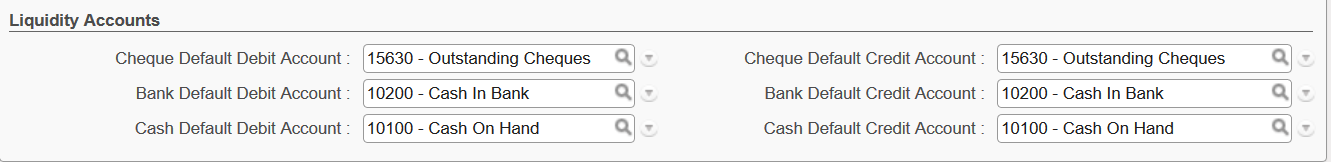
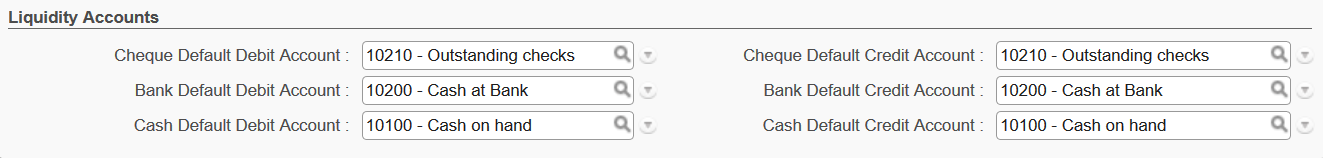
- {Liquidity} accounts are used to book transactions every time there is a liquidity movement in the bank, cash or cheque register.
- {Consolidation} accounts are not currently used in UniField.
- {Closed} accounts are not currently used in UniField.
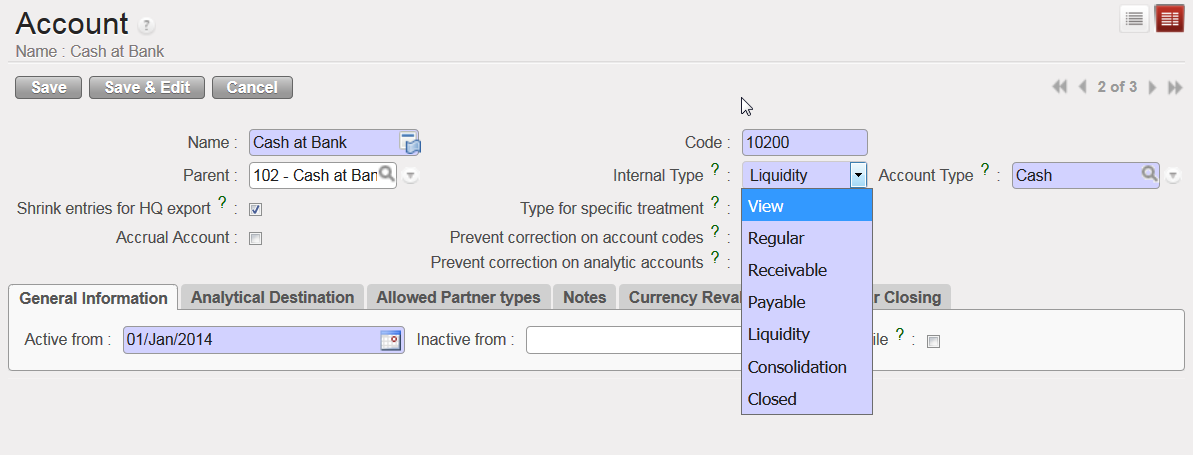 Internal Type options for the accounts
Internal Type options for the accounts
The Type for specific treatment sets attributes triggering specific behaviours for well-defined use cases as detailed below:
- {Internal Transfer} when booking an internal transfer on an account associated to this type for specific treatment, at time of selecting the third party, UniField will display the liquidity journal(s) that will be used as a counterpart and that are defined in a currency other than the register line being created.
- {Internal Transfer (same currency)} when booking an internal transfer on an account associated to this type for specific treatment, at time of selecting the third party, UniField will display the liquidity journal(s) that will be used as a counterpart and that are defined in the same currency as the register line being created.
- {Operational Advance} once the entry is posted in a register, it displays a button called {operational advance} which is a wizard used to close the advance. The third party in this case will be the employee the advance was delivered to.
- {Third party required – Payroll} is used to record the counterpart elements of payroll entries (e.g social security, income taxes accounts) when validating the staff payroll in UniField.
- {Down payment} will let user link an advance requested by a supplier with a purchase order. This function allows you to better track outstanding advance payments to external suppliers.
- {Donation} is used to record donation entries in extra-accounting journals.
- {Reconciliation – Disregard 3rd party} is used to enable reconciliation of entries booked on the same account code with a different third party.
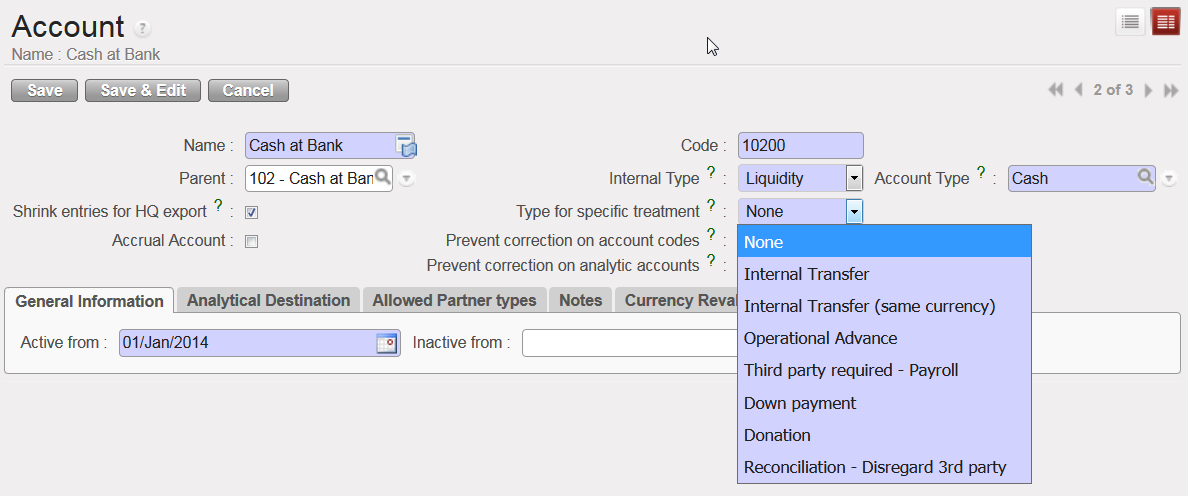 Types for specific treatment
Types for specific treatment
UniField introduces the use of Accrual Accounting. It is a method that recognises economic events (expense or income) regardless of when cash transactions occur and the point of time at which supporting documents are received, with some uncertainty related to the booking (period, exact amount etc.). In UniField the {Accrual Account} attribute will help you semi-automate the creation of accrual entries at month or year-end cut-off. For more information on how to book accrual entries, see Chapter 5 – Searching, Correcting, Closing.
In the Account Form view, the {Accrual Account} box should be checked on balance sheet accounts if the account is used to record accruals. Only accounts with ticked {Accrual account} checkbox are available to be selected for accrual entries.
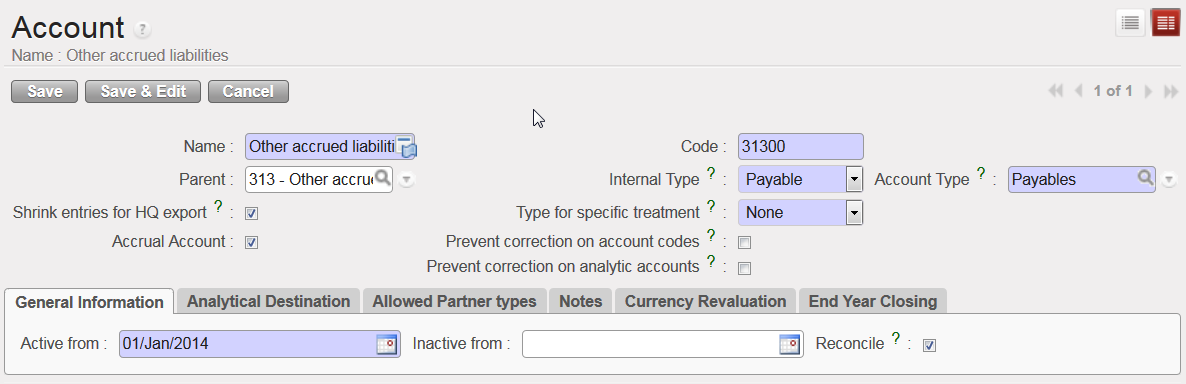
Accrual Account {31300 – Other accrued liabilities} and Accrual Account box checked
In order to easily retrieve accrual accounts when encoding a transaction, an {Accrual Account} filter is available in the G/L accounts list. If you select this button, it will only show a list of accounts that have the {Accrual Account} box ticked.
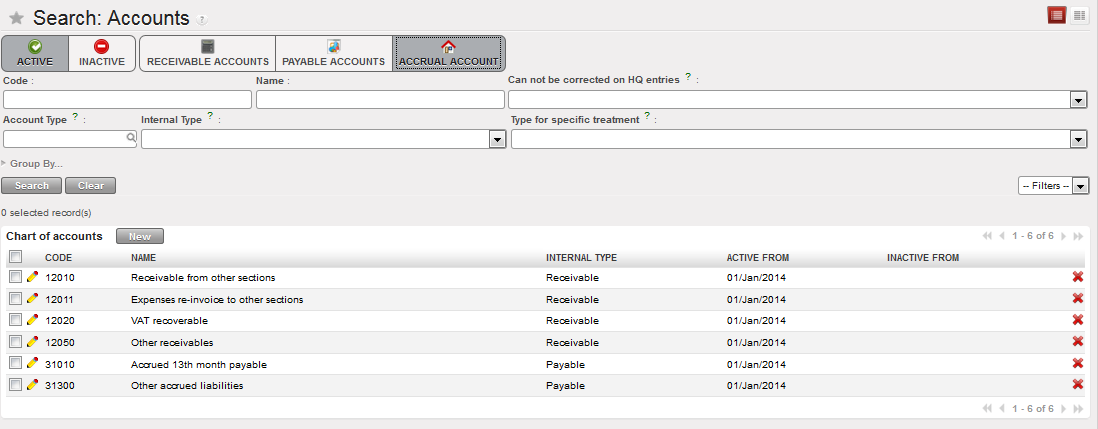 Accrual accounts listed when selecting the filter {Accrual Account}
Accrual accounts listed when selecting the filter {Accrual Account}
Another account feature is linked to the accounting correction. In the Account Form view, there is a {Prevent correction on account codes} box that you need to select if the account must not be corrected at mission level when importing entries from HQ system. There is also a box {Prevent correction on analytic accounts} to tick to disable changes on analytical distribution. Please note if you tick box {Prevent correction on analytic accounts}, {Prevent correction on account codes} will be ticked as well. Check your section’s procedures to define which account codes should not be corrected in UniField at field level.
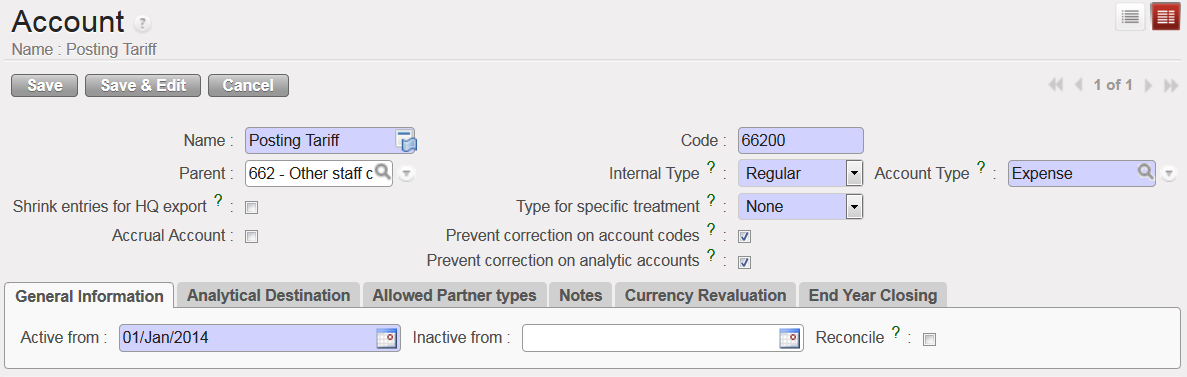
Account {66200} and Analytical Distribution not correctable
If you want to consolidate entries on an account before they are exported to the HQ system, you need to check the {Shrink entries for HQ export} box.
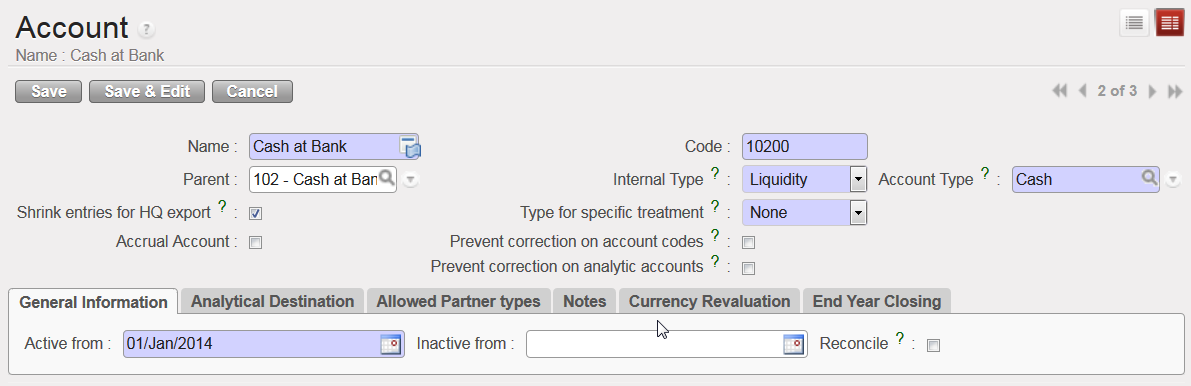 Entries on the account {10200} will be shrinked for HQ export
Entries on the account {10200} will be shrinked for HQ export
As soon as an account is created in your instance, it is automatically activated. The {Active from} date is visible in the {General Information} tab. When the account becomes obsolete, it can be inactivated. The {Inactive from} date must be the following day of the last day entries can be booked in this account, e.g. if an account is used until 31st December 2017, the {Inactive from} date is 1st January 2018.
Active date is taking automatically first day of the current month ,eg, if the account created today 20/06/2018 it will take automatically 01/06/2018.
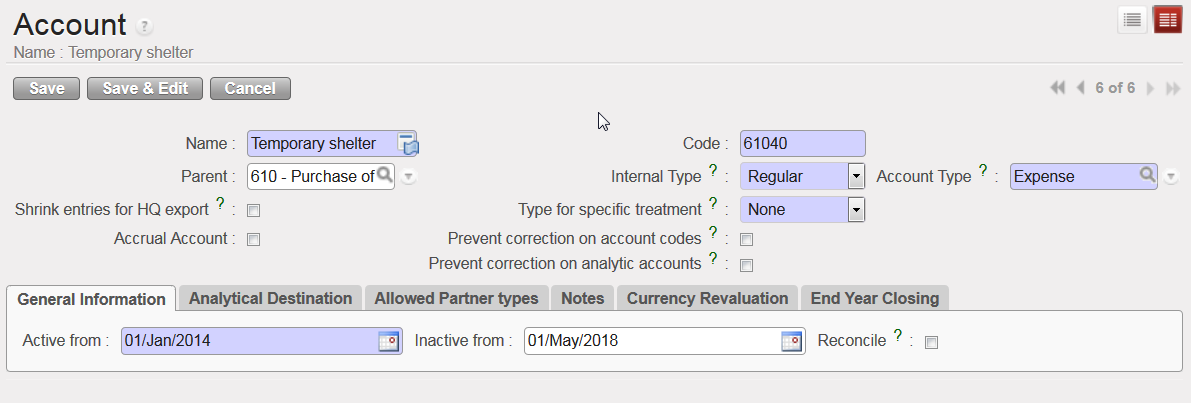 Account 61040 inactive from 1stMay 2018
Account 61040 inactive from 1stMay 2018
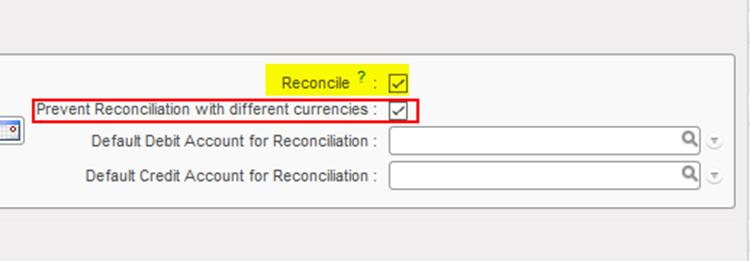
In the {General Information} tab, the {Reconcile} box should be ticked if entries on the account need to be reconciled. In UniField, accounting reconciliations are automatically done for some accounts but for other accounts the user will have to do a manual reconciliation. Account reconciliation is addressed in Chapter 5: Searching, Correcting, Closing.
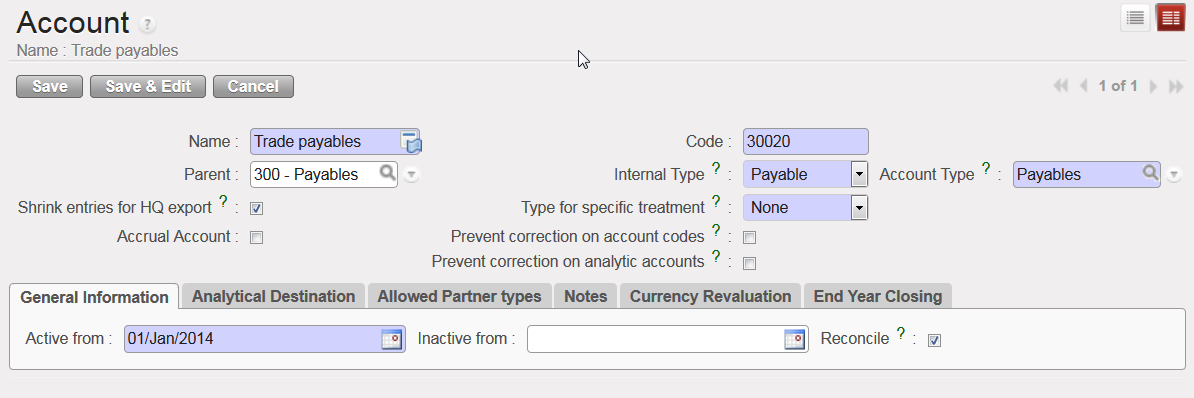
{30020 Trade payables} account, reconcilable
In {Allowed Partner Types} tab, the types of Partners allowed to be used for entries in each account can be edited. By default, all Partner types are selected for all accounts and any restrictions on Partners can be done by unticking the box for the specific Partner Type.
The restriction applies at the time of validating an entry: if a Partner/Account combination is not allowed, the entry cannot be validated. Please check your OCs procedure in regards to any Partner/Account restrictions.
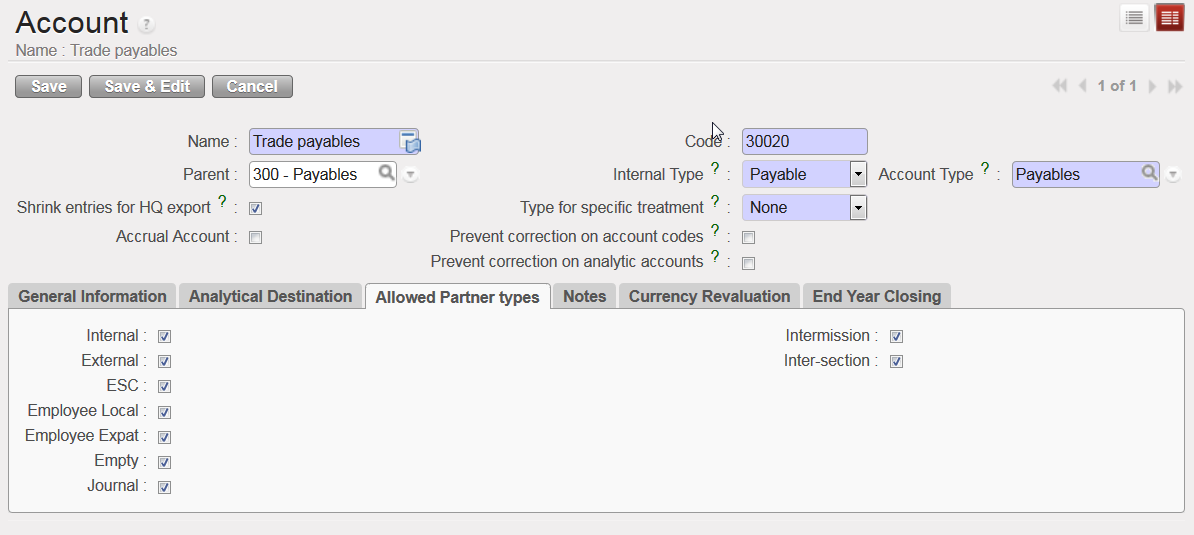 Allowed Partner Types for account 30020
Allowed Partner Types for account 30020
The {End Year Closing} tab relates to a specific Action {Move regular B/S accounts to 0} of the Year-End closing. If the checkbox in this tab is ticked, the Account’s balance is set to 0 with a year-end entry at the time of closing the fiscal year. For further information on Fiscal Year closing, see Chapter 5 – Searching, Correcting, Closing.
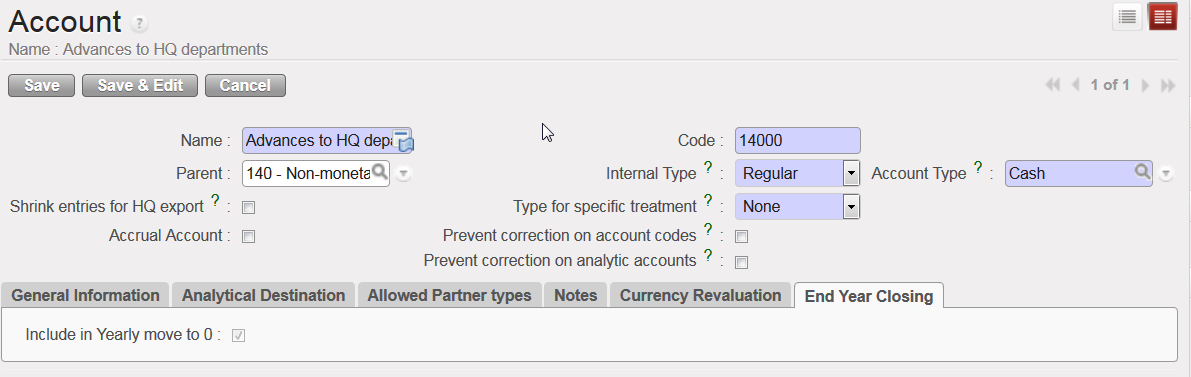 The Account {14000} balance is selected to be set to 0 at Fiscal Year closing
The Account {14000} balance is selected to be set to 0 at Fiscal Year closing
If the checkbox in the {Currency Revaluation} tab is ticked, the selected Account will be included in the month and/or year-end revaluation of the Account balances. Please refer to your OCs policies in regards to currency revaluation practices.
 The Account {10100} is selected to be included in month and year-end currency revaluation
The Account {10100} is selected to be included in month and year-end currency revaluation
How to Manually Create a Financial Account
Manual creation of financial accounts should remain exceptional and based on the section procedures. Once again, it is handled at HQ level as it will synchronize down to all missions.
This example shows the manual creation of an expense account for a boat rental. You must link this new account to the parent account {Transport Freight, Storage} and analytical destination {operations}. Please note that the linkage between the expense accounts and analytical destination is normally done manually once the Chart of Accounts is uploaded and from the Analytic Accounts sub-module (for further detail, please check the UniField IT user manual).
The activation date is input manually in this case.
Go to: Accounting/Financial Accounting/Accounts/Accounts.
- Click on {New} to display a new account Form view.
- In the {Name} field enter {Boat rental} and in the {Code} field enter {65022}.
- In the {Parent} field, click on the magnifying glass
 and in the wizard Search Chart of Accounts type the code {650} in the {Code} field to link this account to the parent account Rental.
and in the wizard Search Chart of Accounts type the code {650} in the {Code} field to link this account to the parent account Rental.
- Once you have typed the code, click on {Search} to bring up results.
- Select the code {650}.
- On the account Form view, select {Regular} in the field {Internal Type}.
- Select {Expense} in the field {Account Type}.
- Select {None} in the field {Type for Specific treatment}.
- Enter an activation date in the {General Information} tab.
- In the {Analytical Destination} tab, enter the default destination code {OPS}.
- Click Save button.
The financial account {Boat rental} is created and linked by default to the analytical destination {Operations}.
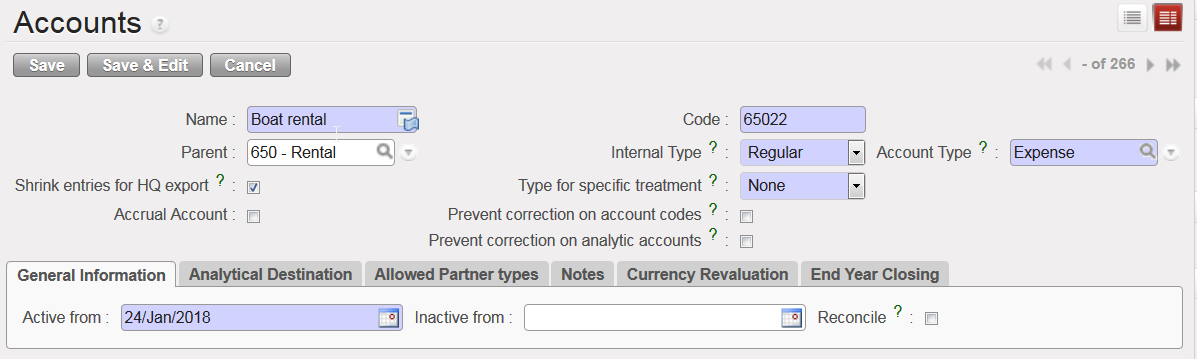 Account 65022 Boat rental Form view
Account 65022 Boat rental Form view
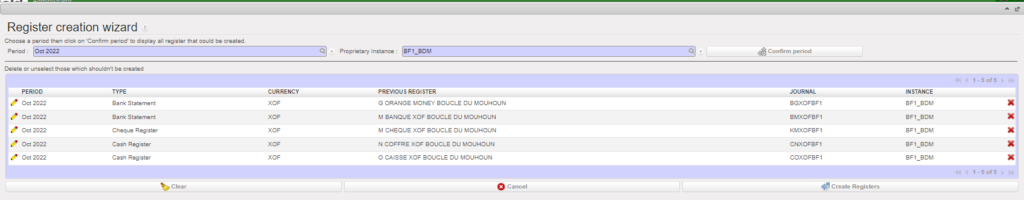
 . You want to create all cash, cheque and bank registers that have active cashboxes and bank accounts.
. You want to create all cash, cheque and bank registers that have active cashboxes and bank accounts.


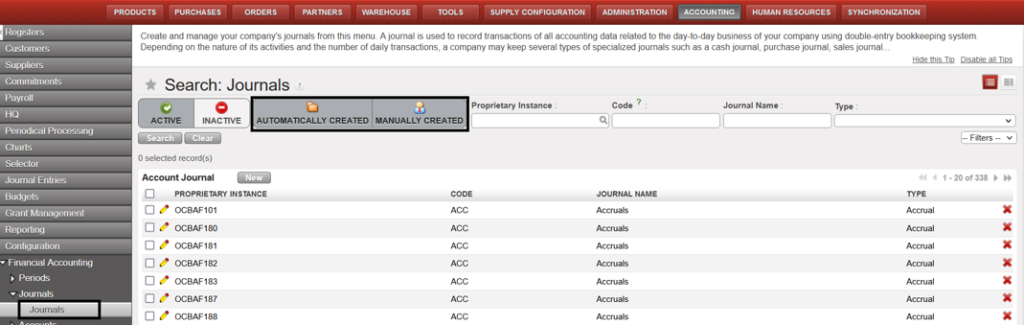
 {Journals Search} view and {New} button
{Journals Search} view and {New} button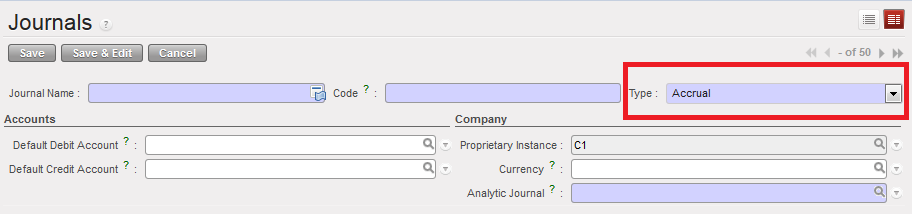 {Journal Form} view and journal type defaults to {Accrual}
{Journal Form} view and journal type defaults to {Accrual}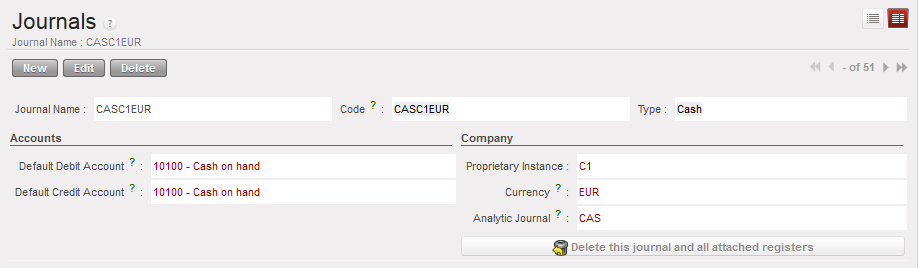
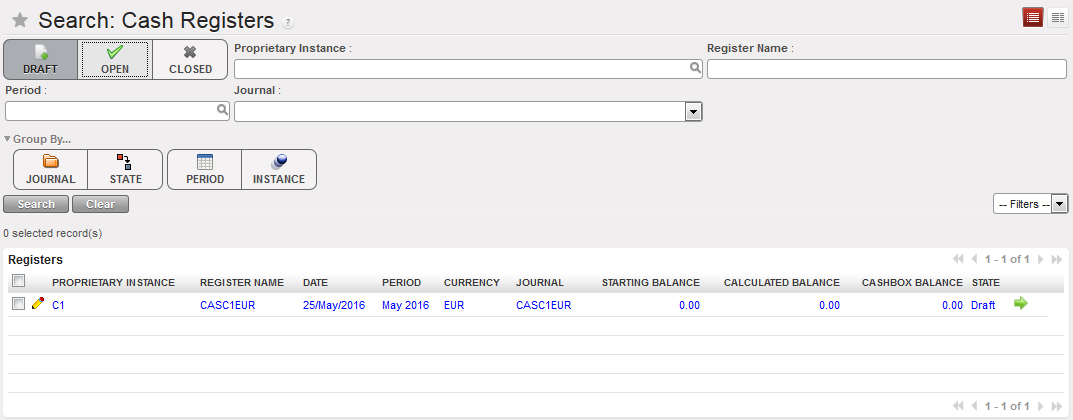 {Cash registers} Search view showing a draft register as the filter Draft was selected
{Cash registers} Search view showing a draft register as the filter Draft was selected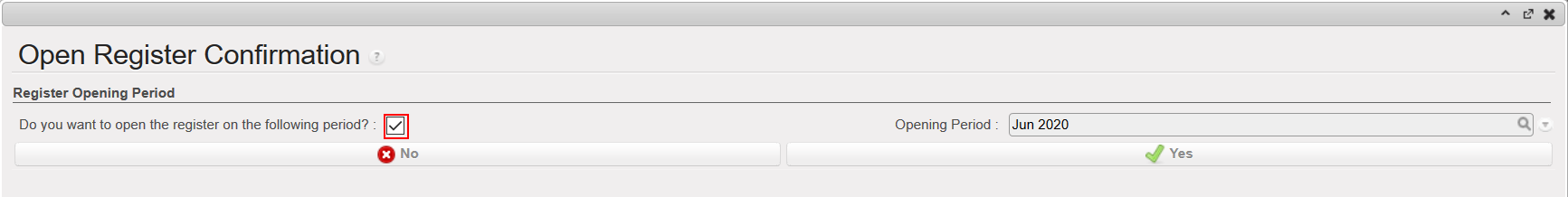 {Open Register confirmation} wizard
{Open Register confirmation} wizard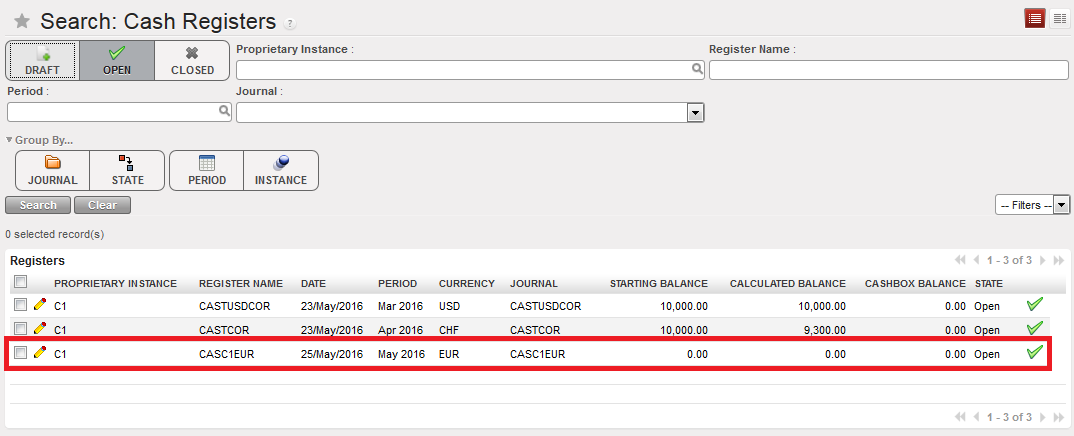 Open Cash register and starting balance of 0.00
Open Cash register and starting balance of 0.00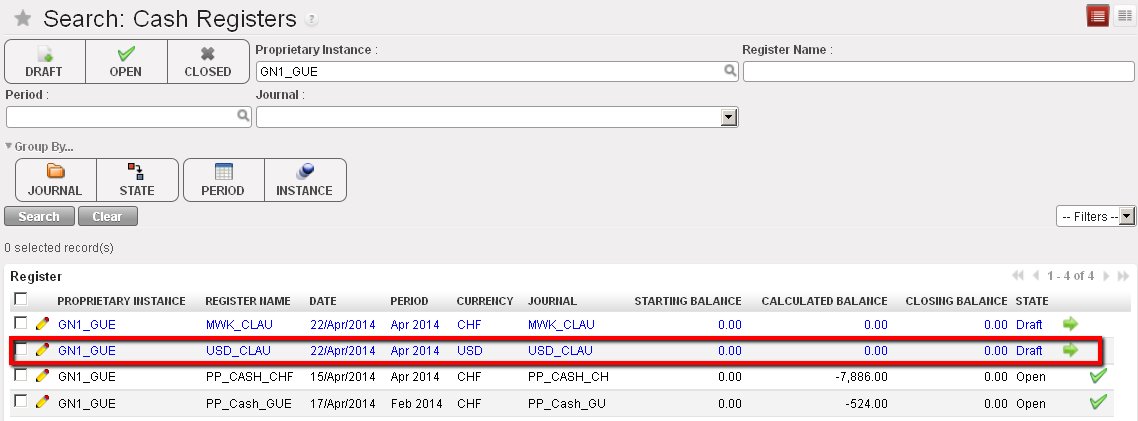 List of Draft cash registers
List of Draft cash registers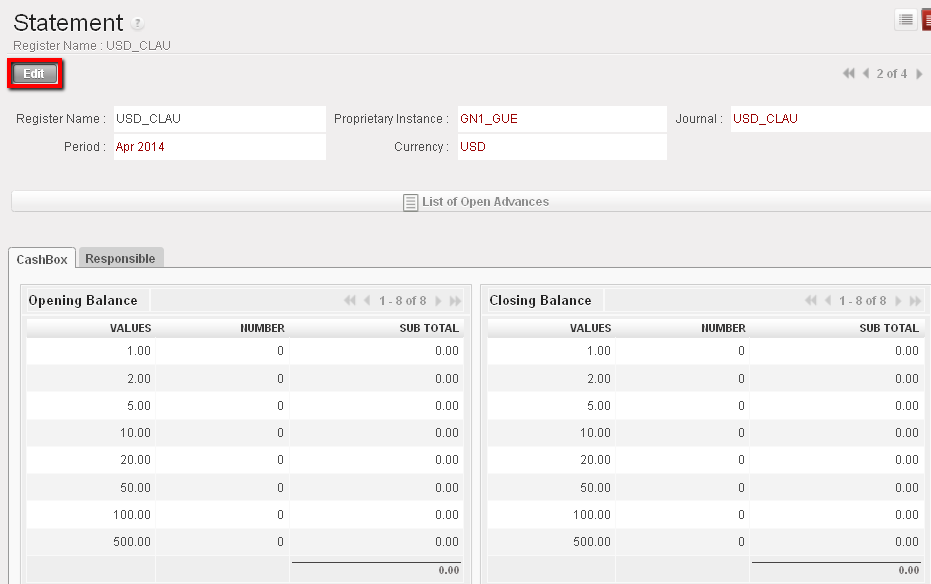 Draft cash register and Cashbox to edit
Draft cash register and Cashbox to edit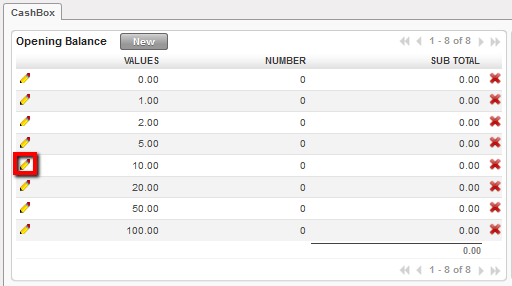
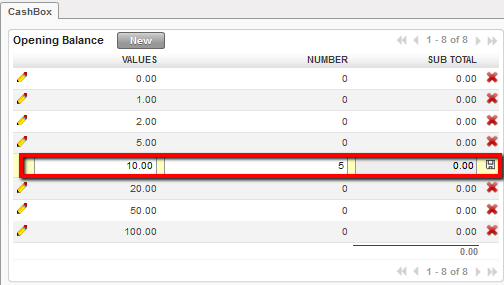
 Opening balance reported in the register cashbox
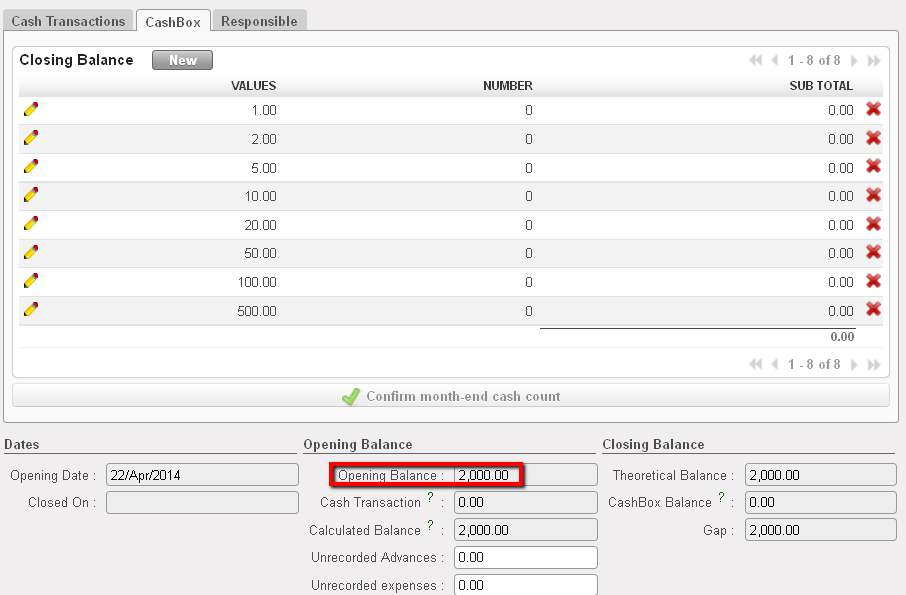
Opening balance reported in the register cashbox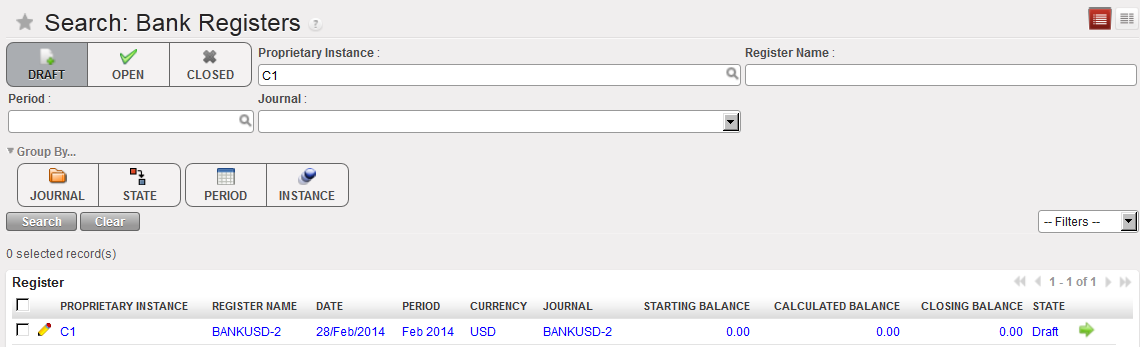 List of Bank cash registers
List of Bank cash registers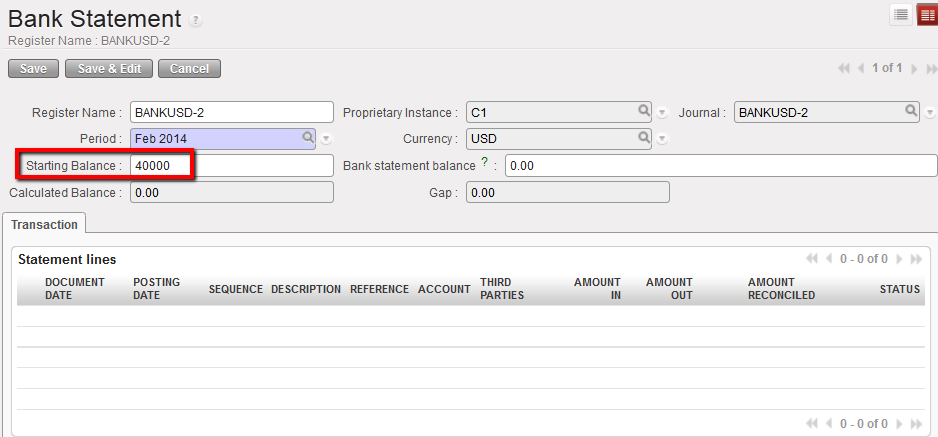 Opening balance reported in the bank register
Opening balance reported in the bank register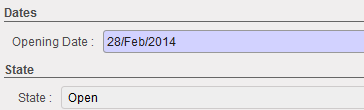
 List of authorised user who can access to this cash register
List of authorised user who can access to this cash register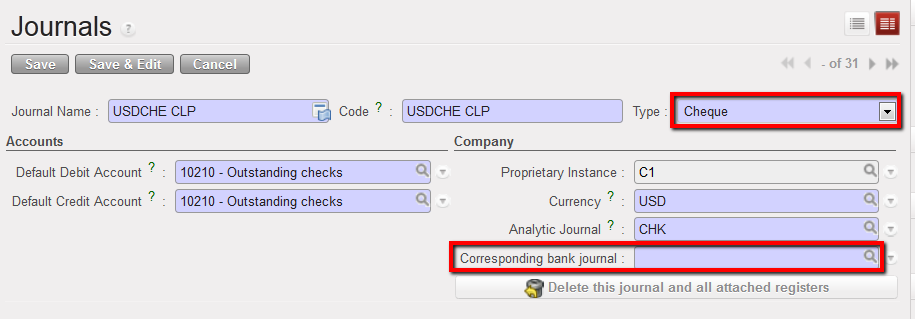 Journal form view and creation of a Cheque journal.
Journal form view and creation of a Cheque journal. 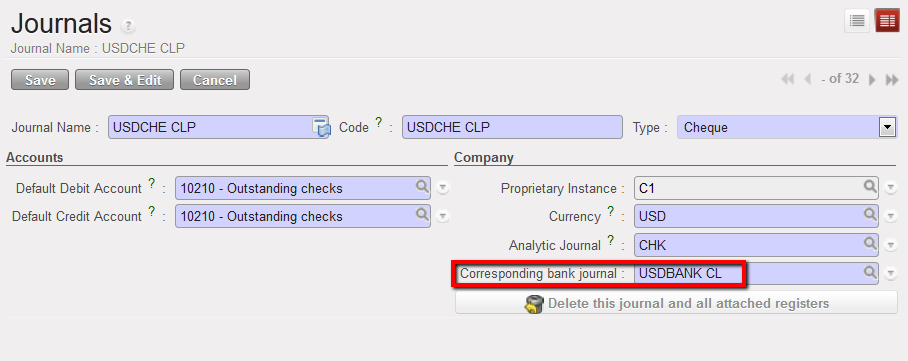 Bank journal associated to a cheque journal
Bank journal associated to a cheque journal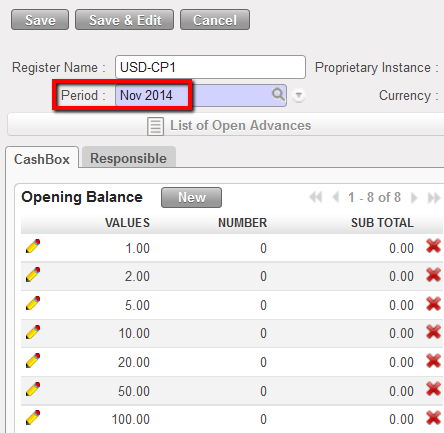
 of the journal line to edit the journal form.
of the journal line to edit the journal form.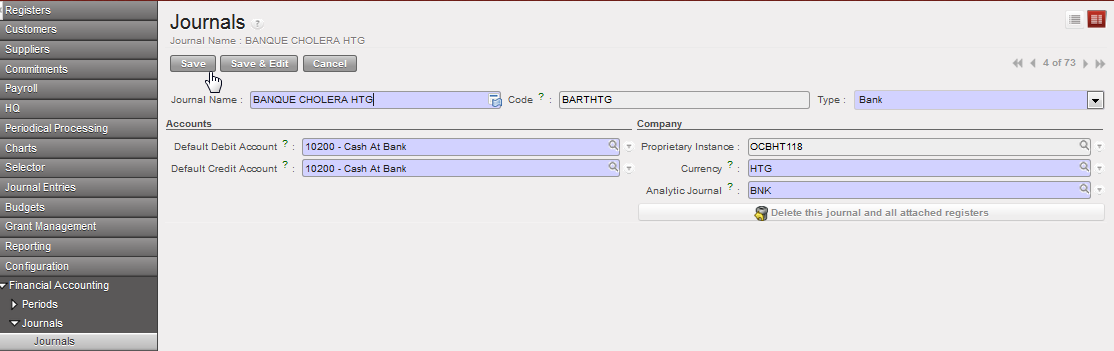

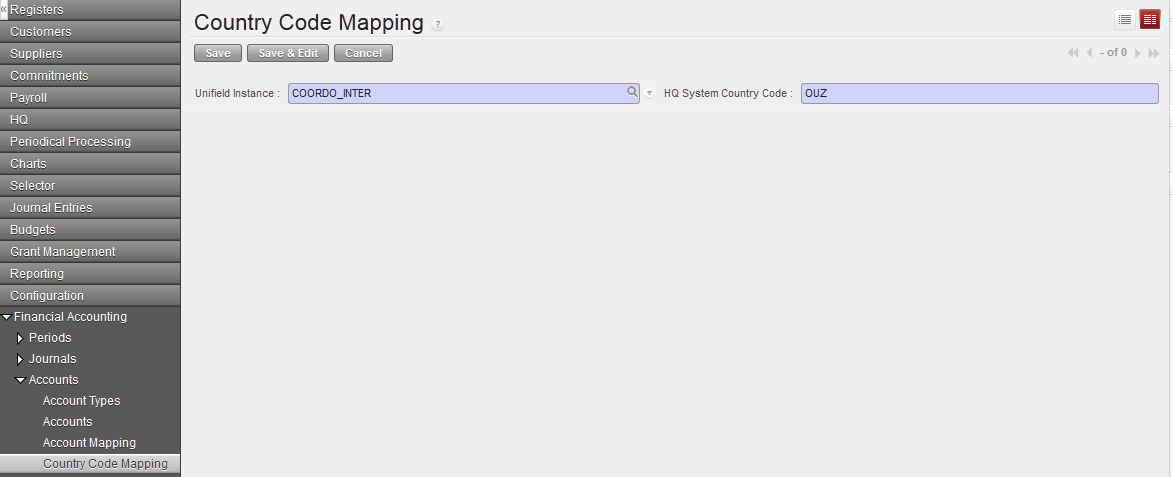 Country code mapping
Country code mapping
 Search Account Mapping view
Search Account Mapping view Import Mappings window
Import Mappings window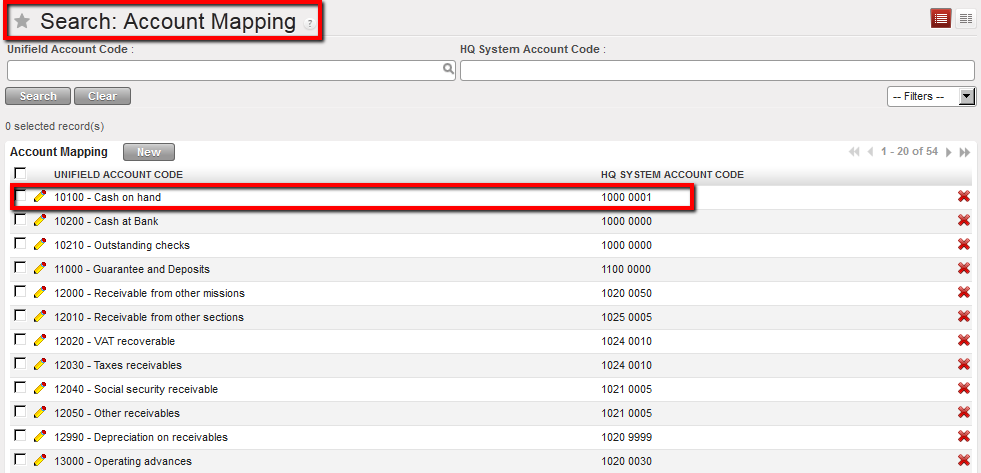 Account Mapping between HQ and Field on B/S accounts is set. For instance, entries booked on the account 10100 in UniField will be automatically recorded on the account 1000 0001 in Axapta.
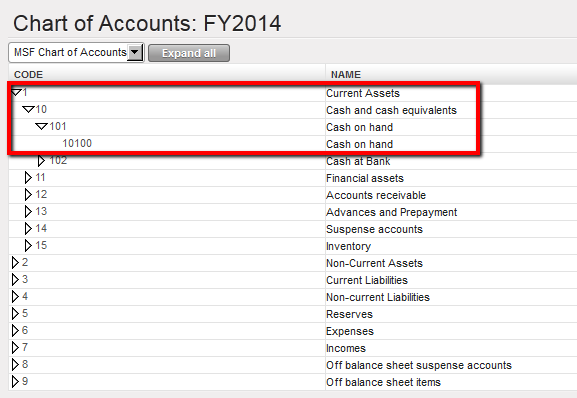
Account Mapping between HQ and Field on B/S accounts is set. For instance, entries booked on the account 10100 in UniField will be automatically recorded on the account 1000 0001 in Axapta. Chart of Accounts window
Chart of Accounts window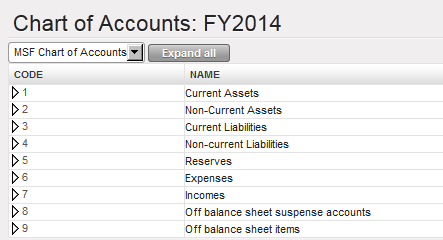



 Account type Asset not correctible
Account type Asset not correctible List of Accounts available in the {Search Accounts} view. The view offers a list of buttons to filter the accounts you search. In this view, only the active accounts are displayed as the Active button is checked.
List of Accounts available in the {Search Accounts} view. The view offers a list of buttons to filter the accounts you search. In this view, only the active accounts are displayed as the Active button is checked. Select the pencil to open the Account form view to see or edit the account’s properties
Select the pencil to open the Account form view to see or edit the account’s properties Account form view and corresponding attributes
Account form view and corresponding attributes Internal Type options for the accounts
Internal Type options for the accounts Types for specific treatment
Types for specific treatment
 Accrual accounts listed when selecting the filter {Accrual Account}
Accrual accounts listed when selecting the filter {Accrual Account}
 Entries on the account {10200} will be shrinked for HQ export
Entries on the account {10200} will be shrinked for HQ export Account 61040 inactive from 1stMay 2018
Account 61040 inactive from 1stMay 2018

 The Account {14000} balance is selected to be set to 0 at Fiscal Year closing
The Account {14000} balance is selected to be set to 0 at Fiscal Year closing  The Account {10100} is selected to be included in month and year-end currency revaluation
The Account {10100} is selected to be included in month and year-end currency revaluation  Account 65022 Boat rental Form view
Account 65022 Boat rental Form view